At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Snowflake DEA-C01 exam questions by Snowflake. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Snowflake SnowPro Advanced: Data Engineer Certification Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Snowflake in their Snowflake DEA-C01 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Snowflake SnowPro Advanced: Data Engineer Certification Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Snowflake DEA-C01 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
A Data Engineer is evaluating the performance of a query in a development environment.
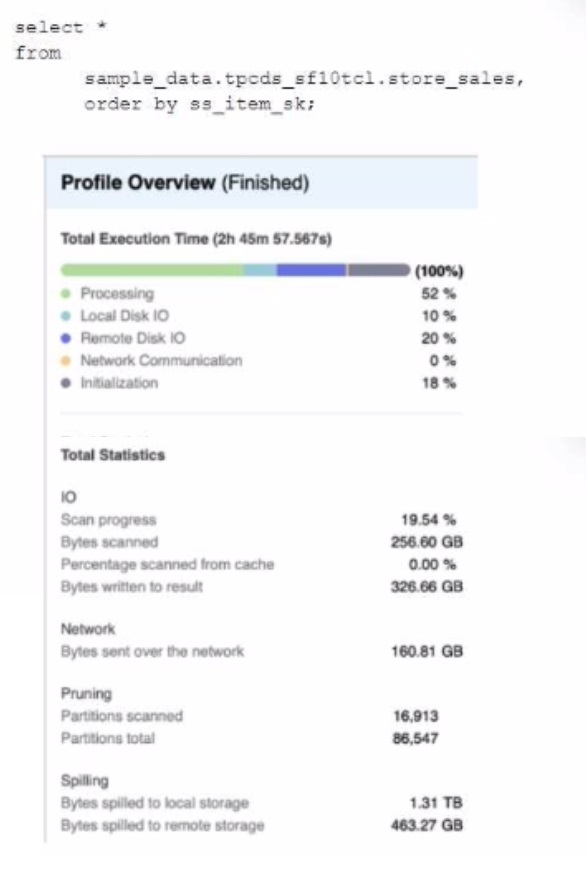
Based on the Query Profile what are some performance tuning options the Engineer can use? (Select TWO)
The performance tuning options that the Engineer can use based on the Query Profile are:
Add a LIMIT to the ORDER BY If possible: This option will improve performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be sorted and returned by the query. The ORDER BY clause requires sorting all rows in the input before returning them, which can be expensive and time-consuming. By adding a LIMIT clause, the query can return only a subset of rows that satisfy the order criteria, which can reduce sorting time and network transfer time.
Create indexes to ensure sorted access to data: This option will improve performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be scanned and filtered by the query. The query contains several predicates on different columns, such as o_orderdate, o_orderpriority, l_shipmode, etc. By creating indexes on these columns, the query can leverage sorted access to data and prune unnecessary micro-partitions or rows that do not match the predicates. This can reduce IO time and processing time.
The other options are not optimal because:
Use a multi-cluster virtual warehouse with the scaling policy set to standard: This option will not improve performance, as the query is already using a multi-cluster virtual warehouse with the scaling policy set to standard. The Query Profile shows that the query is using a 2XL warehouse with 4 clusters and a standard scaling policy, which means that the warehouse can automatically scale up or down based on the load. Changing the warehouse size or the number of clusters will not affect the performance of this query, as it is already using the optimal resources.
Increase the max cluster count: This option will not improve performance, as the query is not limited by the max cluster count. The max cluster count is a parameter that specifies the maximum number of clusters that a multi-cluster virtual warehouse can scale up to. The Query Profile shows that the query is using a 2XL warehouse with 4 clusters and a standard scaling policy, which means that the warehouse can automatically scale up or down based on the load. The default max cluster count for a 2XL warehouse is 10, which means that the warehouse can scale up to 10 clusters if needed. However, the query does not need more than 4 clusters, as it is not CPU-bound or memory-bound. Increasing the max cluster count will not affect the performance of this query, as it will not use more clusters than necessary.
A database contains a table and a stored procedure defined as.
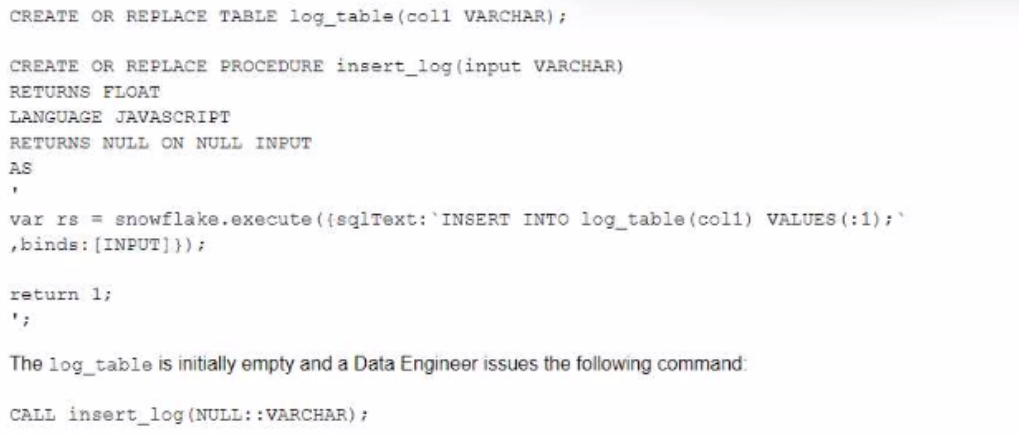
No other operations are affecting the log_table.
What will be the outcome of the procedure call?
The stored procedure is defined with a FLOAT return type and a JavaScript language. The body of the stored procedure contains a SQL statement that inserts a row into the log_table with a value of '1' for col1. The body also contains a return statement that returns 1 as a float value. When the stored procedure is called with any VARCHAR parameter, it will execute successfully and insert one record into the log_table and return 1 as a return value. The other options are not correct because:
The log_table will not be empty after the stored procedure call, as it will contain one record inserted by the SQL statement.
The stored procedure will not return NULL as a return value, as it has an explicit return statement that returns 1.
What is a characteristic of the use of external tokenization?
External tokenization is a feature in Snowflake that allows users to replace sensitive data values with tokens that are generated and managed by an external service. External tokenization allows the preservation of analytical values after de-identification, such as preserving the format, length, or range of the original values. This way, users can perform analytics on the tokenized data without compromising the security or privacy of the sensitive data.
A Data Engineer defines the following masking policy:

....
must be applied to the full_name column in the customer table:

Which query will apply the masking policy on the full_name column?
The query that will apply the masking policy on the full_name column is ALTER TABLE customer MODIFY COLUMN full_name SET MASKING POLICY name_policy;. This query will modify the full_name column and associate it with the name_policy masking policy, which will mask the first and last names of the customers with asterisks. The other options are incorrect because they do not follow the correct syntax for applying a masking policy on a column. Option B is incorrect because it uses ADD instead of SET, which is not a valid keyword for modifying a column. Option C is incorrect because it tries to apply the masking policy on two columns, first_name and last_name, which are not part of the table structure. Option D is incorrect because it uses commas instead of dots to separate the database, schema, and table names
A Data Engineer has developed a dashboard that will issue the same SQL select clause to Snowflake every 12 hours.
---will Snowflake use the persisted query results from the result cache provided that the underlying data has not changed^
Snowflake uses the result cache to store the results of queries that have been executed recently. The result cache is maintained at the account level and is shared across all sessions and users. The result cache is invalidated when any changes are made to the tables or views referenced by the query. Snowflake also has a retention policy for the result cache, which determines how long the results are kept in the cache before they are purged. The default retention period for the result cache is 24 hours, but it can be changed at the account, user, or session level. However, there is a maximum retention period of 14 days for the result cache, which cannot be exceeded. Therefore, if the underlying data has not changed, Snowflake will use the persisted query results from the result cache for up to 14 days.