At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Salesforce Analytics-DA-201 exam questions by Salesforce. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Salesforce Certified Tableau Data Analyst exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Salesforce in their Salesforce Analytics-DA-201 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Salesforce Certified Tableau Data Analyst exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Salesforce Analytics-DA-201 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
You want to add a comment to March 2020 as shown in the following visualization.
You have the following sets in a Tableau workbook
* Top N Customers
* Customers of 2020
* Top N Products
* Sellers of 2020
Which two sets can you combine? Choose two
In Tableau, sets can be combined if they are created from the same dimension. From the options provided, 'Customers of 2020' and 'Top N Customers' are likely created from the same dimension (Customers). Therefore, these two sets can be combined to create a new set that includes or excludes members based on the combined criteria. Combining sets like 'Top N Products' with 'Customers of 2020' would not be feasible unless they are from the same dimension, which is typically not the case.
You have the following visualization.
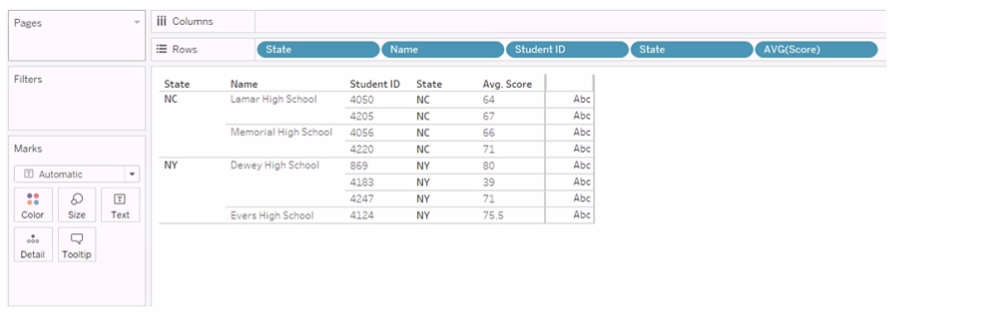
You Create a table calculation named Rank_Score that has a formula of RANK(AVG([Score]), and you drag Rank_Score to Text on the Marks cards.
What is the Rank Score value for Student ID 4220?
To determine the Rank Score value for Student ID 4220, we look at the visualization provided and apply the table calculation of RANK(AVG([Score])). This function will rank the average scores in ascending order by default, with the lowest score receiving the rank of 1.
Based on the provided visualization, the scores for the students are as follows (from lowest to highest average score):
Student ID 4183: 39 (Rank 1)
Student ID 4220: 71 (Rank 6)
Student ID 4247: 71 (Rank 6, same score as ID 4220 so they share the same rank)
Student ID 4124: 75.5
Student ID 4050: 64
Student ID 4205: 67
Student ID 4056: 66
Since Student ID 4220 has an average score of 71, which is the third-highest score, it shares the rank with Student ID 4247. However, since Tableau ranks without gaps, the actual rank assigned is 6, considering that there are two students with a rank of 4 (due to the same average score being the second lowest), making the next rank number 6.
Note: The actual ranks for the highest scores are not provided, but they are not needed to determine the rank for Student ID 4220.
https://help.tableau.com/current/prep/en-us/prep_calculations.htm
You need the top 10 values to appear in a different color. The lop 10 values must be colored dynamically.
What should you do?
You have the following Map.
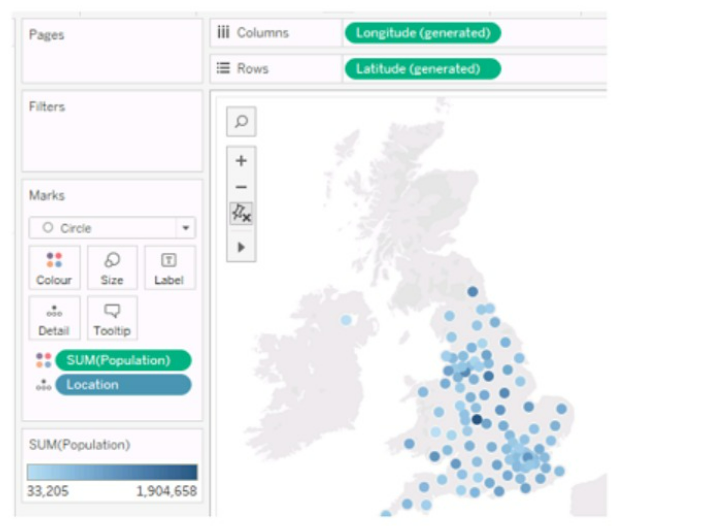
You need the map to appear as shown in the following visualization.
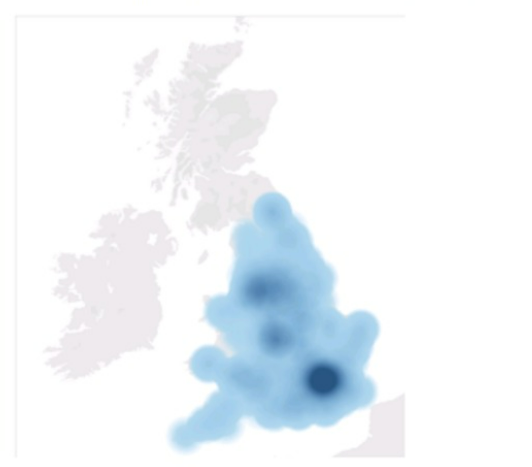
What should you do?
To create a map visualization that shows the concentration of data points in different locations, you need to change the mark type to Density. This will create a heatmap that uses color and size to indicate the density of the data points. You can also adjust the intensity and transparency of the density marks to suit your needs.Reference:The information is based on the following sources:
Create Heatmaps that Show Trends or Density in Tableau
A Data Analyst has a dataset that contains the fallowing rows of sales data.
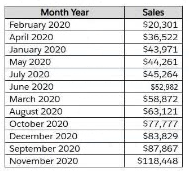
The analyst needs to return a value of TRUE if a month has sales greater than $50,000; otherwise, the formula must return a value of FALSE.
Which two formulas achieve this goal? (Choose two.)