At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Pure Storage FAAA_004 exam questions by Pure Storage. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Pure Storage FlashArray Architect Associate exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Pure Storage in their Pure Storage FAAA_004 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Pure Storage FlashArray Architect Associate exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Pure Storage FAAA_004 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
A customer has presented two workloads that need to be replicated. One is a highly transactional database workload and the other is a VM datastore with tier one applications.
The customer has the following requirements:
* The database workload is highly reliant on storage performance The VM datastore requires zero downtime.
* The customer has advised the two FlashArrays will be 20 miles apart and they are worried that this could impact their internal SLAs.
What replication strategies should be advised for these workloads?
To address the customer's requirements, we need to evaluate the replication strategies offered by Pure Storage FlashArray: ActiveCluster and ActiveDR , and how they align with the specific needs of the two workloads.
Workload Analysis:
Transactional Database Workload :
This workload is highly reliant on storage performance. Any replication strategy must ensure minimal latency and high availability to avoid impacting transactional throughput and response times.
The database workload typically benefits from synchronous replication to maintain consistency and performance across sites.
VM Datastore (Tier 1 Applications) :
This workload requires zero downtime, meaning it must remain accessible even in the event of a site failure. High availability and seamless failover are critical.
The VM datastore can tolerate some level of asynchronous replication as long as it does not compromise availability or recovery objectives.
Replication Strategies:
ActiveCluster :
ActiveCluster is a synchronous replication solution that provides active-active high availability across two FlashArrays. It ensures zero RPO (Recovery Point Objective) and zero RTO (Recovery Time Objective), making it ideal for workloads requiring continuous availability and zero downtime.
ActiveCluster is well-suited for the VM datastore workload because it guarantees seamless failover and high availability, meeting the zero-downtime requirement.
ActiveDR :
ActiveDR is an asynchronous replication solution designed for disaster recovery scenarios. It provides near-zero RPO (typically seconds to minutes) and allows for non-disruptive testing of failover scenarios.
ActiveDR is better suited for the transactional database workload because it minimizes the impact of latency over the 20-mile distance while still maintaining high performance and consistency.
Distance Consideration:
The 20-mile distance between the two FlashArrays introduces latency concerns. Synchronous replication (ActiveCluster) can handle this distance effectively for the VM datastore workload due to its tolerance for slightly higher latency. However, for the transactional database workload, the latency could degrade performance, making ActiveDR a better choice.
Final Recommendation:
Use ActiveCluster for the VM datastore workload to achieve zero downtime and high availability.
Use ActiveDR for the transactional database workload to balance performance and disaster recovery needs over the 20-mile distance.
Pure Storage ActiveCluster Documentation :
Explains the synchronous replication capabilities and use cases for ActiveCluster.
Pure Storage ActiveDR Documentation :
Details the asynchronous replication features and disaster recovery use cases for ActiveDR.
Pure Storage Best Practices for Replication :
Provides guidance on selecting the appropriate replication strategy based on workload requirements and distance considerations.
Pure Storage Replication Best Practices
Pure Storage Architectural Guides :
Covers architectural considerations for deploying ActiveCluster and ActiveDR in multi-site environments.
Pure Storage Architectural Guides
This approach ensures that both workloads meet their respective SLAs while addressing the customer's concerns about distance and performance.
Refer to the exhibit.
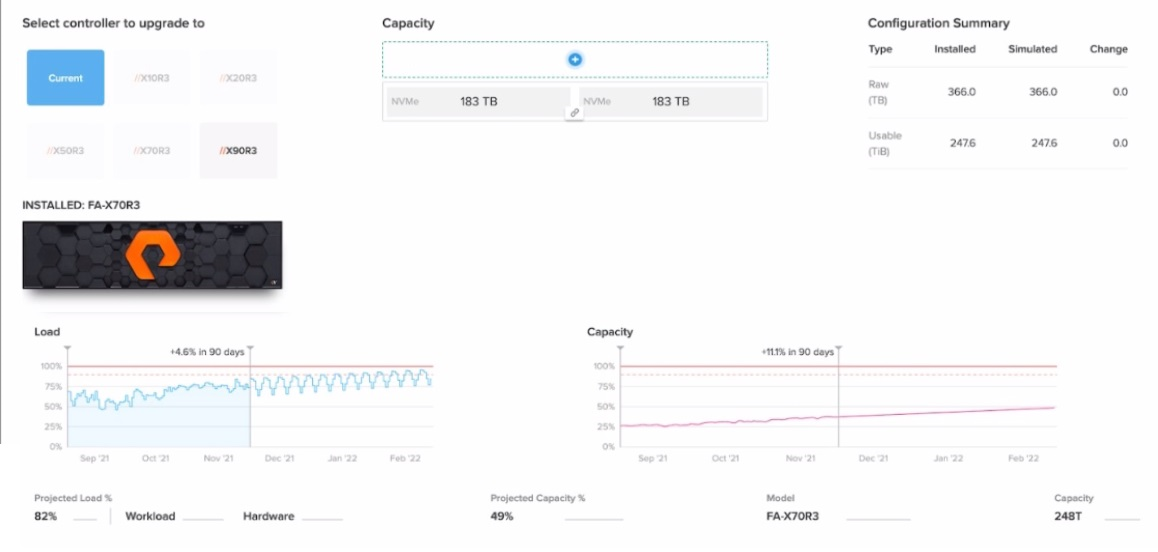
A customer is assessing the health of their FlashArray.
What should the customer discuss with their SE based on this information?
Based on the exhibit (referenced via the link), the customer should discuss adding a second shelf of NVMe DirectFlash modules with their SE. This recommendation is based on the assumption that the exhibit indicates the array is nearing its capacity limits or requires additional storage to accommodate future growth.
Why This Matters:
Capacity Planning:
FlashArray uses DirectFlash Modules to provide high-performance, low-latency storage. If the array is approaching its physical capacity, adding a second shelf of NVMe modules is the most effective way to expand storage without requiring a full hardware upgrade.
This approach ensures the array can continue to meet the customer's growing storage needs while maintaining performance and reliability.
Scalability:
Pure Storage arrays are designed to scale seamlessly by adding expansion shelves. This allows customers to increase capacity without disrupting operations or replacing existing hardware.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . Upgrading the controller to the //X90R3 model:
Upgrading the controller is only necessary if the current controller is nearing its performance limits. The exhibit does not indicate performance bottlenecks, so this step is likely unnecessary.
C . Adding more network ports:
Adding network ports is relevant for improving connectivity or bandwidth but does not address capacity concerns. If the array is running out of storage space, adding network ports will not resolve the issue.
Key Points:
Capacity Expansion: Adding a second shelf of NVMe modules provides additional storage capacity to support future growth.
Non-Disruptive Scaling: Expansion shelves can be added without downtime, ensuring continuous availability.
Cost Efficiency: Avoids unnecessary upgrades or replacements, optimizing costs while meeting capacity requirements.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'Expanding FlashArray Capacity with DirectFlash Modules'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Scaling Storage with FlashArray Expansion Shelves'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Best Practices for Capacity Planning and Expansion'
Which Pure Storage offering can be deployed in AWS?
The Pure Storage offering that can be deployed in AWS is Cloud Block Store .
Why This Matters:
Cloud Block Store:
Cloud Block Store is a cloud-native block storage solution that runs in public clouds like AWS and Azure.
It provides enterprise-grade storage features, including deduplication, compression, and thin provisioning, while seamlessly integrating with on-premises FlashArray environments.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . ObjectEngine:
ObjectEngine is a backup and recovery solution designed for rapid restores and backups. It is not a storage solution that can be deployed in AWS.
C . CloudSnap:
CloudSnap is a feature that offloads snapshots to cloud storage (e.g., AWS S3 or Azure Blob). It is not a standalone storage solution but rather a feature of FlashArray.
Key Points:
Cloud Block Store: Provides block storage in AWS with enterprise-grade features.
Integration: Seamlessly integrates with on-premises FlashArray environments for hybrid cloud architectures.
Scalability: Enables scalable and cost-effective storage in the cloud.
Pure Storage Cloud Block Store Documentation: 'Deploying Cloud Block Store in AWS'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Hybrid Cloud Architectures with FlashArray and Cloud Block Store'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Cloud Block Store Use Cases and Deployment'
A System Administrator has a FlashArray//X70R3. They need to add a backup element as part of their data protection strategy. They have the following requirements:
* The solution should be offsite
* Cost needs to be kept as low as possible
* The backup needs to be stored in a different location from their current FlashArray
* Restore times are not a concern
Which solution should the SE recommend to the System Administrator?
The System Administrator requires an offsite backup solution that is cost-effective, stores data in a different location from the current FlashArray, and does not prioritize restore times. The best solution to recommend is CloudSnap to a public cloud provider .
Why This Matters:
CloudSnap:
CloudSnap is a feature that offloads snapshots to cloud storage providers like AWS S3 or Azure Blob.
It is highly cost-effective because customers only pay for the cloud storage they use, and it eliminates the need for additional on-premises hardware.
Since restore times are not a concern, CloudSnap's slower restore process compared to on-premises solutions is acceptable.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . ActiveCluster to a FlashArray//C60:
ActiveCluster provides synchronous replication for high availability but does not meet the requirement for an offsite backup solution. Additionally, it is more expensive than CloudSnap.
B . ActiveDR to a FlashArray//C60:
ActiveDR provides asynchronous replication for disaster recovery but requires additional hardware (FlashArray//C60), which increases costs. It is less cost-effective than CloudSnap for backup purposes.
Key Points:
Cost Efficiency: CloudSnap leverages cloud storage, minimizing upfront and ongoing costs.
Offsite Storage: Ensures backups are stored in a different location from the primary FlashArray.
Restore Times: CloudSnap's slower restore process is acceptable given the customer's requirements.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'CloudSnap for Offsite Backups'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Cost-Effective Backup Strategies with FlashArray'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Choosing the Right Backup Solution for Your Workload'
A manufacturing customer is running Oracle volumes on their existing //X90R3 array and would like to use FlashArray for their Windows file shares. They are asking if it is feasible to do this.
How should the SE respond?
The SE should respond that the customer can use their current FlashArray for Windows file shares alongside their existing Oracle workloads. Pure Storage FlashArray is a versatile platform capable of supporting multiple workloads, including block storage for databases (e.g., Oracle) and file services for Windows file shares.
Why This Matters:
FlashArray Versatility:
Pure Storage FlashArray supports both block and file workloads through its integrated architecture. While FlashArray is primarily known for block storage, it can also support file workloads using FA File Services , which provides NFS and SMB protocols for file sharing.
The customer does not need to migrate their Windows file servers or upgrade their hardware unless there are specific capacity or performance constraints.
Current Array Feasibility:
Assuming the existing //X90R3 array has sufficient capacity and performance headroom, it can handle the additional workload without requiring upgrades.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . The customer should migrate their Windows file servers to Pure:
While migrating file servers to Pure Storage can provide benefits like simplified management and improved performance, it is not a requirement. The customer can continue using their existing file servers while leveraging FlashArray for block storage.
B . The customer needs to upgrade to XL to be able to use FA File:
Upgrading to a higher-end model like FlashArray//XL is unnecessary unless the current array lacks the required capacity or performance for the additional workload. The //X90R3 is fully capable of supporting FA File Services.
Key Points:
Versatility: FlashArray can support both block and file workloads simultaneously.
No Immediate Upgrades Needed: The current array can likely handle the additional workload without requiring hardware changes.
Workload Consolidation: Using a single platform for multiple workloads simplifies infrastructure and reduces costs.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'FA File Services Overview'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Consolidating Workloads on FlashArray'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Supporting Multiple Workloads with FlashArray'