At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Juniper JN0-636 exam questions by Juniper. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Juniper Security, Professional exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Juniper in their Juniper JN0-636 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Juniper Security, Professional exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Juniper JN0-636 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
You are asked to detect domain generation algorithms
Which two steps will accomplish this goal on an SRX Series firewall? (Choose two.)
According to the Juniper documentation, the steps to detect domain generation algorithms (DGA) on an SRX Series firewall are as follows:
set services security-metadata-streaming policy
Attach the security-metadata-streaming policy to a security zone. A security zone is a logical grouping of interfaces that have similar security requirements. You can attach the security-metadata-streaming policy to a security zone by using the following command:
set security zones security-zone <zone-name> services security-metadata-streaming policy
The following steps are not required or incorrect:
Exhibit:
You are troubleshooting a firewall filter shown in the exhibit that is intended to log all traffic and block
only inbound telnet traffic on interface ge-0/0/3.
How should you modify the configuration to fulfill the requirements?
To modify the configuration to fulfill the requirements, you need to modify the log-all term to add the next term action. The other options are incorrect because:
Enter the configuration mode: user@host> configure
Navigate to the firewall filter hierarchy: user@host# edit firewall family inet filter block-telnet
Add the next term action to the log-all term: user@host# set term log-all then next term
Commit the changes: user@host# commit
Your company uses non-Juniper firewalls and you are asked to provide a Juniper solution for zero-day malware protection. Which solution would work in this scenario?
Juniper ATP Cloud provides zero-day malware protection for non-Juniper firewalls. It's a cloud-based service that analyzes files and network traffic to detect and prevent known and unknown (zero-day) threats. It uses a combination of static and dynamic analysis techniques, as well as machine learning, to detect and block malicious files, even if they are not known to traditional anti-virus software. It also provides real-time visibility and detailed forensics for incident response and remediation.
Exhibit
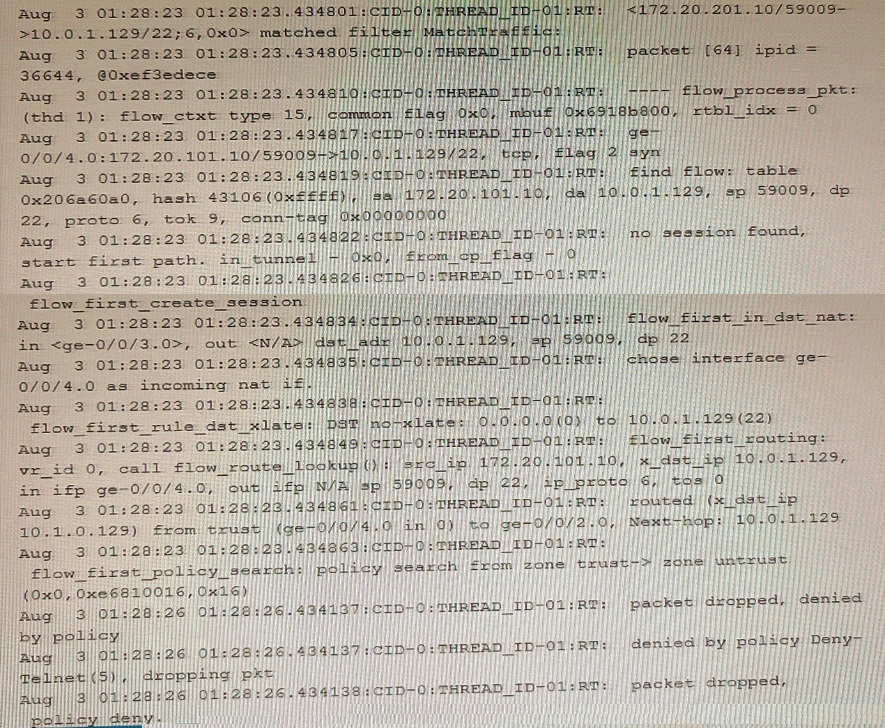
Which two statements are correct about the output shown in the exhibit. (Choose two.)
The source address is translated because the traceoptions output shows that the source IP address 192.168.5.2 is translated to 192.168.100.1 and the source port 0 is translated to 14777. The traceoptions output also shows the flag flow_first_src_xlate, which indicates that this is the first time that source NAT is applied to this session.
The packet is an SSH packet because the traceoptions output shows that the application protocol is tcp/22, which is the default port for SSH. The traceoptions output also shows the flag flow_tcp_syn, which indicates that this is the first packet of a TCP connection.
traceoptions (Security NAT) | Junos OS | Juniper Networks
[SRX] How to interpret Flow TraceOptions output for NAT troubleshooting
You are asked to share threat intelligence from your environment with third party tools so that those
tools can be identify and block lateral threat propagation from compromised hosts.
Which two steps accomplish this goal? (Choose Two)
To share threat intelligence from your environment with third party tools, you need to enable Juniper ATP Cloud to share threat intelligence and configure application tokens in the Juniper ATP Cloud to limit who has access. The other options are incorrect because:
Therefore, the correct answer is B and C. You need to enable Juniper ATP Cloud to share threat intelligence and configure application tokens in the Juniper ATP Cloud to limit who has access. To do so, you need to perform the following steps:
Threat Intelligence Open API Setup Guide