At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Juniper JN0-281 exam questions by Juniper. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Juniper Data Center, Associate exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Juniper in their Juniper JN0-281 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Juniper Data Center, Associate exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Juniper JN0-281 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Which state in the adjacency process do OSPF routers check the MTU size?
In OSPF, routers exchange link-state information in different stages to establish full adjacency. The MTU size is checked during the Exchange state.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
OSPF Adjacency Process:
OSPF routers go through multiple stages when forming an adjacency: Down, Init, 2-Way, ExStart, Exchange, Loading, and Full.
Exchange State:
During the Exchange state, OSPF routers exchange Database Description (DBD) packets to describe their link-state databases. The MTU size is checked at this stage to ensure both routers can successfully exchange these packets without fragmentation.
If there is an MTU mismatch, the routers may fail to proceed past the Exchange state.
Juniper Reference:
MTU Checking in OSPF: Junos uses the Exchange state to check for MTU mismatches, ensuring that routers can properly exchange database information without packet fragmentation issues.
A generated route is configured under which hierarchy?
A generated route in Junos OS is configured under the [edit routing-options] hierarchy.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Generated Routes:
A generated route is created based on the presence of more specific routes in the routing table. It acts as a summary route and is generated when any of its contributing routes are active. This is commonly used to create aggregate routes in OSPF, BGP, or other protocols.
Configuration Hierarchy:
The configuration for generated routes is placed under [edit routing-options], where other static and routing policies are also defined.
Command Example:
set routing-options generate route 10.10.0.0/16
Juniper Reference:
Routing Options: Juniper routers use the routing-options hierarchy to configure generated routes and other static routing behaviors.
What is the main purpose of Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)?
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) is a network protocol used to detect failures in the network path between two devices quickly.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Path Failure Detection:
BFD provides a low-overhead mechanism for detecting failures in forwarding paths across Layer 3 networks. It is much faster than traditional routing protocol timers and can detect failures within milliseconds.
BFD in Routing:
BFD can be integrated with routing protocols like OSPF, BGP, or IS-IS to trigger a faster convergence when a network path goes down.
Juniper Reference:
BFD Configuration: Juniper devices use BFD to monitor network paths and ensure fast failure detection, enhancing network resilience.
What information in the Ethernet header is used to populate the bridging table?
The source MAC address in the Ethernet header is used to populate the bridging table (also called the MAC address table) on a switch. When a frame arrives at a switch, the switch examines the source MAC address and records it along with the ingress port in its MAC address table.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Learning Process:
When an Ethernet frame arrives on a switch port, the switch looks at the source MAC address and adds this MAC address to the MAC table along with the port it was received on. This process is called MAC learning.
Purpose:
The switch uses this information to determine the correct port to send frames destined for that MAC address in future transmissions, thus ensuring efficient Layer 2 forwarding.
Juniper Reference:
Ethernet Switching: Juniper switches use source MAC addresses to build and maintain the MAC address table, which is essential for Layer 2 switching.
Exhibit:
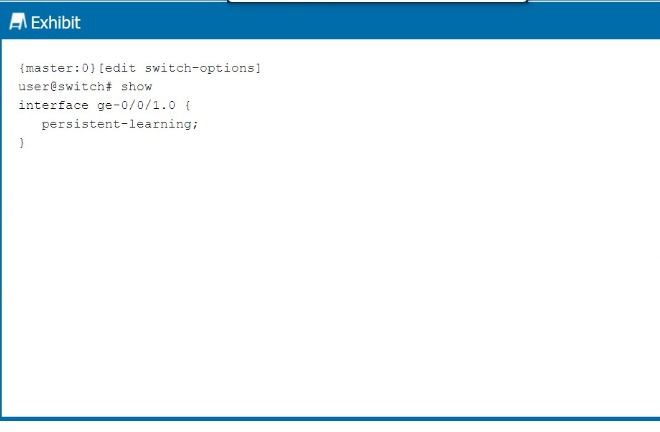
Referring to the exhibit, which behavior does this configuration enable on the ge-0/0/1.0 interface?
The configuration in the exhibit shows the persistent-learning feature enabled on interface ge-0/0/1.0.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Persistent Learning:
Persistent-learning ensures that the MAC addresses learned on the interface are retained in the Ethernet-switching table, even after a device reboot. This prevents the need to re-learn MAC addresses after the device restarts, improving stability and reducing downtime.
Use Case:
This feature is particularly useful in environments where the re-learning of MAC addresses could cause temporary disruptions or delays in communication, such as in critical Layer 2 network segments.
Command Example:
set switch-options interface ge-0/0/1.0 persistent-learning
Juniper Reference:
Persistent MAC Learning: In Junos, enabling persistent-learning ensures that learned MAC addresses are not lost during reboots, contributing to smoother network operations in environments where stability is crucial.