At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Huawei H12-831_V1.0 exam questions by Huawei. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Huawei HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Huawei in their Huawei H12-831_V1.0 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Huawei HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Huawei H12-831_V1.0 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
On the OSPF network shown in the figure, R1 and R2 use OSPF to communicate with each other through Loopback0. In addition:
MPLS LDP is enabled on R1 and R2.
The LDP transport address is the IP address of Loopback0.
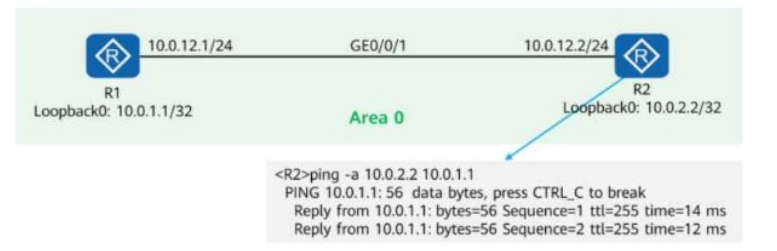
A network engineer finds that an LDP session cannot be established between R1 and R2 and runs diagnostic commands (shown in the figure) to locate the fault.
Given this, which of the following are possible causes of the fault?
Options:
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
1. Understanding MPLS LDP (Label Distribution Protocol)
LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) runs over TCP port 646.
LDP uses the transport address (Loopback0 in this case) to establish TCP sessions between neighbors.
For an LDP session to be established, both routers must:
Enable LDP on the interface (GE0/0/1).
Allow TCP traffic on port 646 (used for LDP adjacency formation).
2. Analyzing the Issue and Possible Causes
The figure shows a successful ping from R2 to R1's Loopback0 (10.0.1.1/32).
This means basic IP connectivity between R1 and R2 is working.
OSPF is properly advertising Loopback0 addresses between the routers.
The problem must be related to LDP itself, not general IP reachability.
3. Evaluating Each Answer Option
Option A: 'R1's GE0/0/1 rejects packets with the destination IP address 10.0.2.2.'
Incorrect.
The ping test in the figure shows successful replies from 10.0.1.1 to 10.0.2.2, meaning packets to 10.0.2.2 are not being rejected.
This is NOT the cause of the LDP failure.
Option B: 'MPLS LDP is not enabled on R2's GE0/0/1.'
Correct.
If LDP is not enabled on R2's GE0/0/1, then R1 and R2 cannot form an LDP session.
MPLS LDP must be enabled on both interfaces for label exchange.
This is a valid cause of the issue.
Option C: 'R2's GE0/0/1 rejects packets with TCP destination port 646.'
Correct.
LDP operates over TCP port 646, so if R2's GE0/0/1 has a firewall or ACL blocking TCP port 646, then LDP will fail.
Blocking TCP 646 on R2's interface would prevent the session from establishing.
This is another valid cause of the issue.
Option D: 'R1's GE0/0/1 rejects packets with UDP destination port 646.'
Incorrect.
LDP does not use UDP; it uses TCP port 646.
This is not a valid cause of the issue.
Final Answer:
B and C are correct.
HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology Reference:
MPLS LDP Session Establishment and TCP 646 Dependency
How OSPF Advertises Loopback0 for LDP Transport
Common LDP Debugging Techniques and ACL Issues
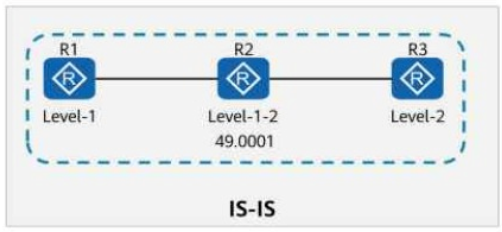
On the IS-IS network shown in the figure, R1 imports a default route using the default-route-advertise always level-1 command. Which of the following statements are true?
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
Understanding the IS-IS Levels and Default Route Advertisement:
R1 is a Level-1 router
R2 is a Level-1-2 router (meaning it connects both Level-1 and Level-2 areas)
R3 is a Level-2-only router
Step 1: What Does 'default-route-advertise always level-1' Do?
This command forces R1 to advertise a default route (0.0.0.0/0) to all its Level-1 IS-IS neighbors, regardless of whether R1 has a default route in its routing table.
Since R1 is a Level-1 router, it does not participate in Level-2 routing, meaning it relies on R2 (a Level-1-2 router) for external connectivity.
Step 2: Checking the Routing Tables
R1: Since it is only a Level-1 router and does not receive a default route from any higher-level router, it does not have a default route in its own routing table. (D is correct)
R2: Since R1 advertises the default route at Level-1, R2 (a Level-1-2 router) receives this default route in its Level-1 database. (B is correct)
R3: R3 is a Level-2-only router, and default routes are not automatically leaked between Level-1 and Level-2 unless explicitly configured.
Since no explicit route leaking configuration is mentioned, R3 will not have the default route (C is incorrect).
A is incorrect because the command successfully advertises a default route from R1 to Level-1 neighbors like R2.
Final Answer: B, D
HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 -- IS-IS Default Route Advertisement
IS-IS Routing Level-1 and Level-2 Behavior
IS-IS Route Leaking and Default Route Propagation
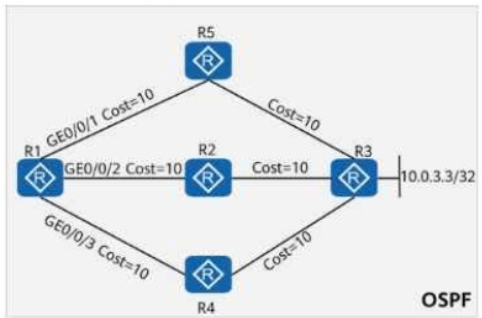
On the OSPF network shown in the figure, the cost values of links are marked. OSPF IP FRR is enabled on R1, and the maximum load-balancing 8 command is configured in the OSPF process. If a service passes through the path R1 R5 R3 to reach 10.0.3.3/32, which of the following is the backup outbound interface for the service?
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
Step 1: Identify the Primary Path
The shortest OSPF cost to 10.0.3.3/32 from R1 is through R5:
R1 R5 (Cost 10) R3 (Cost 10) = Total Cost 20
The primary outbound interface from R1 to R5 is GE0/0/1.
Step 2: Identify the Backup Path (OSPF IP FRR & ECMP)
OSPF IP Fast Reroute (FRR) provides a backup next-hop in case the primary link (R1 R5) fails.
A feasible backup path must have a cost equal to or close to the primary path, but it must avoid the same failure point.
Alternative Path Calculation:
Path 1 (R1 R2 R3)
R1 R2 (Cost 10), R2 R3 (Cost 10) Total Cost = 20
Uses interface GE0/0/2 on R1.
Path 2 (R1 R4 R3)
R1 R4 (Cost 10), R4 R3 (Cost 10) Total Cost = 20
Uses interface GE0/0/3 on R1.
Final Decision on the Backup Interface
Since both paths R1 R2 R3 and R1 R4 R3 have equal costs, either can be used for backup.
However, R1 R2 R3 shares a direct cost path with R5, meaning it may not be preferred as a full FRR backup.
The best backup outbound interface in this scenario is GE0/0/3 (R1 R4 R3).
Final Answer: C (GE0/0/3)
HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 -- OSPF IP FRR (Fast Reroute) Mechanism
OSPF Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) and Backup Route Selection
OSPF Route Calculation and Best-Path Selection
On the OSPF network shown in the figure, area 1 and area 2 are common areas. The IP address of Loopback0 on R5 is 10.0.5.5/32, and OSPF is enabled on this interface. If the abr-summary 10.0.5.0 255.255.255.0 command is run in area 2 (where R1 resides), which of the following routers have the route 10.0.5.0/24 in their routing tables?
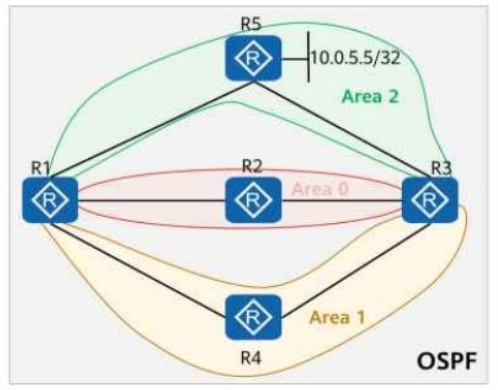
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
Step 1: Understanding OSPF Areas and Summarization
Loopback0 on R5 has IP 10.0.5.5/32 and is advertised into OSPF.
The abr-summary 10.0.5.0 255.255.255.0 command is applied in area 2 on R1, which means:
Instead of advertising individual host routes (like 10.0.5.5/32), R1 advertises the summarized route 10.0.5.0/24 into Area 0 (Backbone).
This summarized route is then propagated into other areas via Area 0 (Backbone).
Step 2: Analyzing the Routing Table of Each Router
R5 (Originating Router in Area 2)
R5 only knows 10.0.5.5/32 because it's the originating router.
The abr-summary command does not affect R5 itself.
R5 does not have 10.0.5.0/24.
R1 (ABR for Area 2, Summarizing the Route)
R1 creates and advertises 10.0.5.0/24 into Area 0.
This summary route is sent to other areas via Area 0.
R2 (Connected to Area 0 & Area 1)
Since R2 is part of Area 0 (Backbone), it receives 10.0.5.0/24 from R1.
R2 has 10.0.5.0/24 in its routing table.
R3 (Connected to Area 0 & Area 2)
Since R3 is also connected to Area 0, it receives the summary route 10.0.5.0/24 from R1.
R3 has 10.0.5.0/24 in its routing table.
R4 (In Area 1, which is not directly connected to Area 2)
R4 belongs to Area 1, and unless explicitly advertised through inter-area summarization, it will not have 10.0.5.0/24.
Since no specific mention of summary advertisement into Area 1 is made, R4 does not get 10.0.5.0/24.
R4 does not have 10.0.5.0/24.
Final Answer: R2, R3 (Option B, C)
HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 -- OSPF Route Summarization
OSPF Inter-Area Route Advertisement via ABRs
OSPF Backbone (Area 0) Behavior and Route Distribution
On the OSPF network shown in the figure, a network engineer finds that R1 and R2 have the same router ID, and both have imported default routes (with the default-route-advertise always command configured). Given this, which of the following statements is false?