At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the HPE6-A85 exam questions by HP. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Associate Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by HP in their HPE6-A85 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Associate Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the HPE6-A85 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Which statement is correct when comparing 5 GHz and 6 GHz channels with identical channel widths?
While both 5 GHz and 6 GHz channels can provide similar throughputs, the higher frequency of the 6 GHz band means its signals have a shorter range and are more attenuated by obstacles compared to 5 GHz signals. This results in 5 GHz channels generally being able to travel longer distances than 6 GHz channels under similar conditions, although both can support high data rates for connected clients.
A network technician is testing a new SSID for a branch office. They are able to connect, get an IP address, and resolve DNS names. However, they are not able to browse the internet.
On the existing SSID at the branch, connectivity to the internet works as expected on the same VLAN as the new SSID. The wireless client should have received a new role to allow internet access.
What should the network technician verify to ensure both SSIDs function in a similar way?
When a network technician encounters an issue where a new SSID does not allow internet access despite successful connectivity and DNS resolution, they should verify the firewall policies associated with the new SSID. The firewall policies must include rules that permit traffic to and from the internet and should be correctly ordered to ensure that they are applied as intended. Since the existing SSID functions correctly, comparing the firewall rules between the two can be a useful method of troubleshooting.
What is the correct command to add a static route to a class-c-network 10.2.10.0 via a gateway of 172.16.1.1?
To add a static route in network devices, including Aruba switches, the correct command format generally includes the destination network, subnet mask (or CIDR notation for the mask), and the next-hop IP address. The command 'ip route 10.2.10.0/24 172.16.1.1' correctly specifies the destination network '10.2.10.0' with a class C subnet mask indicated by '/24', and '172.16.1.1' as the next-hop IP address. This command is succinct and follows the standard syntax for adding a static route in many network operating systems, including ArubaOS-CX. The other options either have incorrect syntax or include additional unnecessary parameters that are not typically part of the standard command to add a static route.
You have been asked to troubleshoot failed connectivity between a local subnet in the HQ Office and a remote subnet in the Branch Office. PC1 is unable to ping PC2.
Use the provided topology and show command output to identify the reason for the failure:
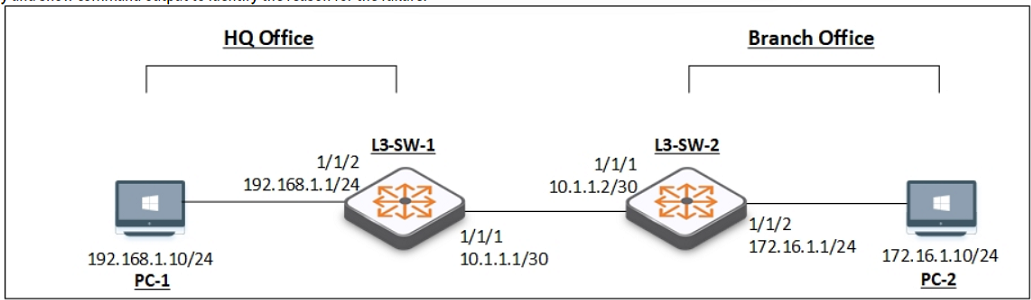
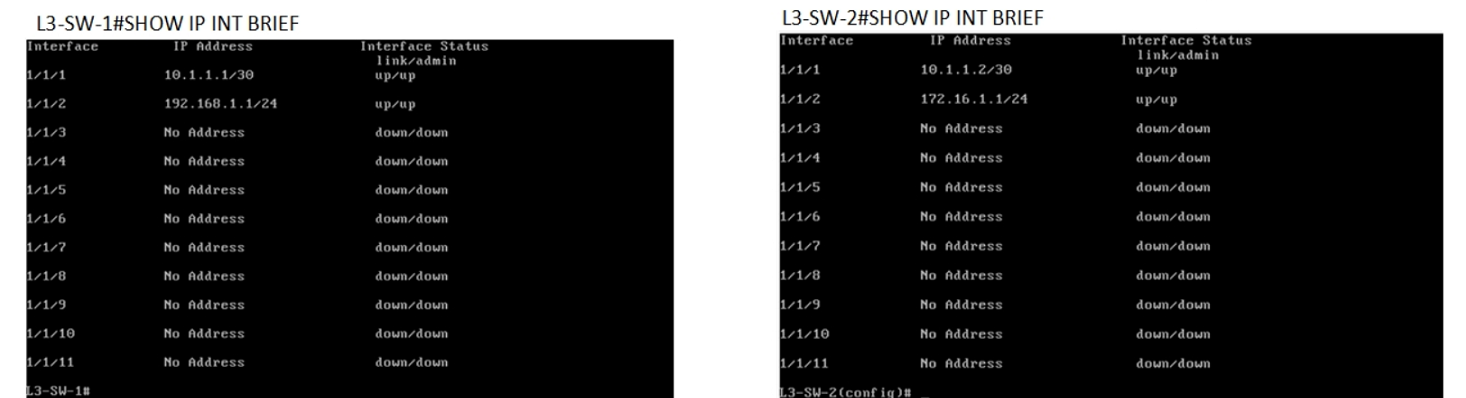
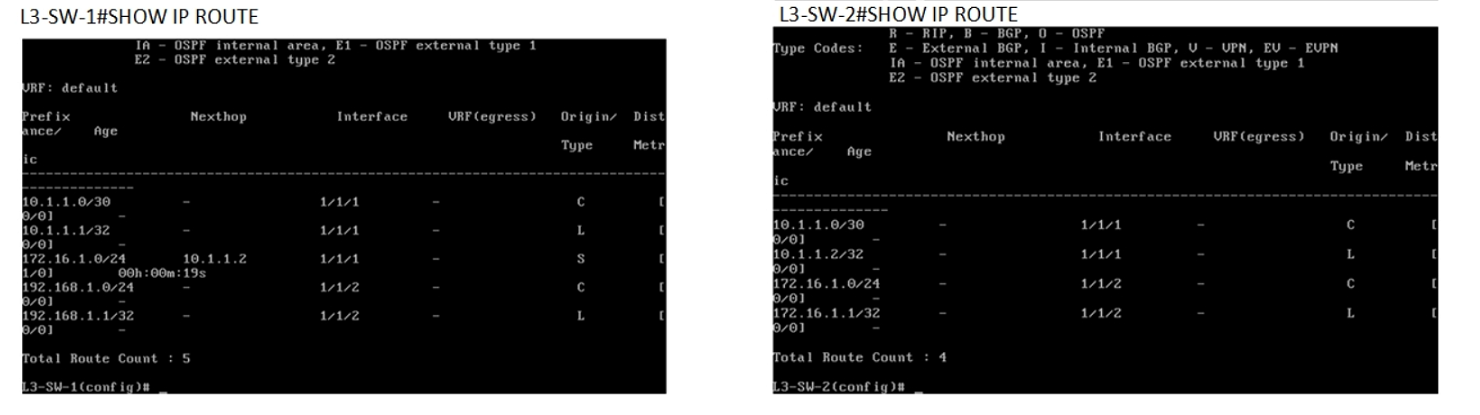
Using the provided topology and show command output, it can be determined that L3-SW-2 in the Branch Office does not have a route to reach the subnet where PC1 resides (192.168.1.0/24 in the HQ Office). L3-SW-1 in the HQ Office has a route to the Branch Office subnet (172.16.1.0/24), but without the reciprocal route on L3-SW-2, traffic from the Branch Office will not be able to reach the HQ Office subnet, hence PC1 cannot ping PC2.