At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the HPE6-A78 exam questions by HP. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the HP Aruba Certified Network Security Associate Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by HP in their HPE6-A78 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their HP Aruba Certified Network Security Associate Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the HPE6-A78 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
What purpose does an initialization vector (IV) serve for encryption?
An initialization vector (IV) is a random or pseudo-random value used in encryption algorithms to enhance security. It is commonly used in symmetric encryption modes like Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) or Counter (CTR) modes with algorithms such as AES, which is used in WPA3 and other Aruba security features.
Option B, 'It makes encryption algorithms more secure by ensuring that the same plaintext and key can produce different ciphertext,' is correct. The primary purpose of an IV is to introduce randomness into the encryption process. When the same plaintext is encrypted with the same key multiple times, the IV ensures that the resulting ciphertext is different each time. This prevents attackers from identifying patterns in the ciphertext, which could otherwise be used to deduce the plaintext or key. For example, in AES-CBC mode, the IV is XORed with the first block of plaintext before encryption, and each subsequent block is chained with the previous ciphertext, ensuring unique outputs.
Option A, 'It enables programs to convert easily-remembered passphrases to keys of a correct length,' is incorrect. This describes a key derivation function (KDF), such as PBKDF2, which converts a passphrase into a cryptographic key of the correct length. An IV is not involved in key derivation.
Option C, 'It helps parties to negotiate the keys and algorithms used to secure data before data transmission,' is incorrect. This describes a key exchange or handshake protocol (e.g., Diffie-Hellman or the 4-way handshake in WPA3), not the role of an IV. The IV is used during the encryption process, not during key negotiation.
Option D, 'It enables the conversion of asymmetric keys into keys that are suitable for symmetric encryption,' is incorrect. This describes a process like hybrid encryption (e.g., using RSA to encrypt a symmetric key), which is not the purpose of an IV. An IV is used in symmetric encryption to enhance security, not to convert keys.
The HPE Aruba Networking Wireless Security Guide states:
'An initialization vector (IV) is a random value used in symmetric encryption algorithms like AES to enhance security. The IV ensures that the same plaintext encrypted with the same key produces different ciphertext each time, preventing attackers from identifying patterns in the ciphertext. In WPA3, for example, the IV is used in AES-GCMP encryption to ensure that each packet is encrypted uniquely, even if the same data is sent multiple times.' (Page 28, Encryption Fundamentals Section)
Additionally, the HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide notes:
'The initialization vector (IV) in encryption algorithms like AES-CBC or AES-GCMP makes encryption more secure by ensuring that identical plaintext encrypted with the same key results in different ciphertext. This randomness prevents pattern analysis attacks, which could otherwise compromise the security of the encryption.' (Page 282, Wireless Encryption Section)
:
HPE Aruba Networking Wireless Security Guide, Encryption Fundamentals Section, Page 28.
HPE Aruba Networking AOS-8 8.11 User Guide, Wireless Encryption Section, Page 282.
===========
What is a benefit or using network aliases in ArubaOS firewall policies?
In ArubaOS firewall policies, using network aliases allows administrators to manage groups of IP addresses more efficiently. By associating multiple IPs with a single alias, any changes made to the alias (like adding or removing IP addresses) are automatically reflected in all firewall rules that reference that alias. This significantly simplifies the management of complex rulesets and ensures consistency across security policies, reducing administrative overhead and minimizing the risk of errors.
You are configuring ArubaOS-CX switches to tunnel client traffic to an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC). What should you do to enhance security for control channel communications between the switches and the MC?
When configuring ArubaOS-CX switches to tunnel client traffic to an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC), securing the control channel communications is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity. Option B is the correct answer as it involves configuring a long, random PAPI security key that matches on both the switches and the MC. The PAPI (Policy Access Point Interface) protocol is used for secure communication between Aruba devices, and employing a robust, randomized security key significantly enhances the security of the control channel. This setup prevents potential interception or manipulation of the control traffic between the devices.
:
ArubaOS-CX Security Configuration Guide
Aruba Networks Official Documentation
Refer to the exhibit.
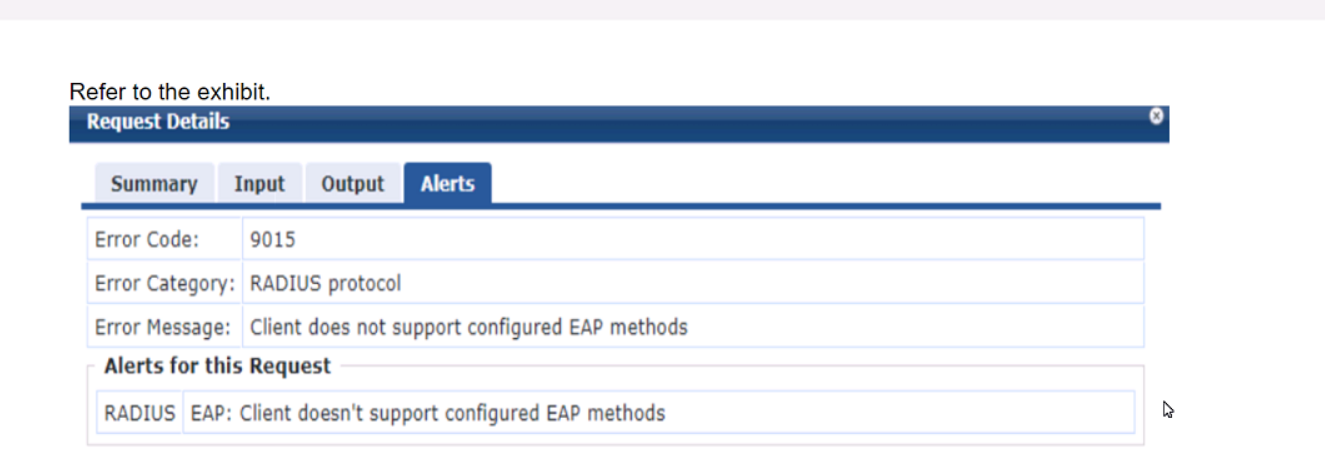
A company has an Aruba Instant AP cluster. A Windows 10 client is attempting to connect a WLAN that enforces WPA3-Enterprise with authentication to ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). CPPM is configured to require EAP-TLS. The client authentication fails. In the record for this client's authentication attempt on CPPM, you see this alert.
What is one thing that you check to resolve this issue?
In the context of WPA3-Enterprise with EAP-TLS authentication, the error message 'Client doesn't support configured EAP methods' suggests that the client is not able to complete the EAP-TLS authentication process. EAP-TLS requires that both the server (in this case, CPPM) and the client have a valid certificate for mutual authentication. Windows 10 does support EAP-TLS natively, so options A, C, and D can be ruled out.
The most likely reason for the authentication failure is that the client device does not have the correct client certificate installed, which is required to establish a TLS session with the server. Therefore, ensuring that the client has a valid certificate installed that matches the server's requirements is the correct step to resolve this issue.
How should admins deal with vulnerabilities that they find in their systems?
When vulnerabilities are identified in systems, it is crucial for administrators to act immediately to mitigate the risk of exploitation by attackers. The appropriate response involves applying fixes, such as software patches or configuration changes, to close the vulnerability. This proactive approach is necessary to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the system resources and data. It's important to prioritize these actions based on the severity and exploitability of the vulnerability to ensure that the most critical issues are addressed first. :
Best practices in system security management.