At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE7_ZTA-7.2 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 7 - Zero Trust Access 7.2 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE7_ZTA-7.2 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 7 - Zero Trust Access 7.2 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE7_ZTA-7.2 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Which statement is true about FortiClient EMS in a ZTNA deployment?
In a ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) deployment, FortiClient EMS:
A) Uses endpoint information to grant or deny access to the network: FortiClient EMS plays a critical role in ZTNA by using information about the endpoint, such as its security posture and compliance status, to determine whether to grant or deny network access.
The other options do not accurately represent the role of FortiClient EMS in ZTNA:
B) Provides network and user identity authentication services: While it contributes to the overall ZTNA strategy, FortiClient EMS itself does not directly provide authentication services.
C) Generates and installs client certificates on managed endpoints: Certificate management is typically handled by other components in the ZTNA framework.
D) Acts as ZTNA access proxy for managed endpoints: FortiClient EMS does not function as an access proxy; its role is more aligned with endpoint management and policy enforcement.
FortiClient EMS in Zero Trust Network Access Deployment.
Role of FortiClient EMS in ZTNA.
Exhibit.
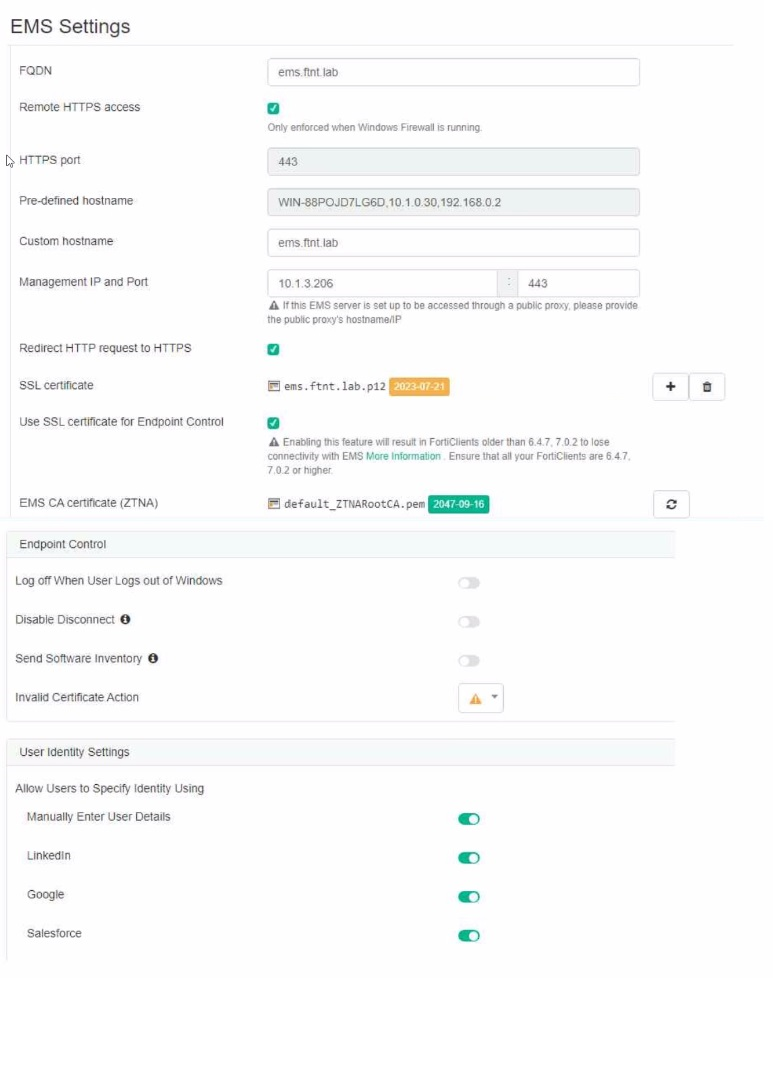
Which statement is true about the configuration shown in the exhibit?
The exhibit shows the EMS Settings where various configurations related to network security are displayed. Option C is correct because, in the settings, it is indicated that HTTPS port is used (which operates over TCP) and SSL certificates are involved in securing the connection, implying the use of TLS for encryption and secure communication between FortiClient and FortiClient EMS.
Option A is incorrect because the domain that FortiClient is connecting to does not have to match the domain to which the certificate is issued. The certificate is issued by the ZTNA CA, which is a separate entity from the domain. The certificate only contains the device ID, ZTNA tags, and other information that are used to identify and authenticate the device.
Option B is incorrect because if the FortiClient EMS server certificate is invalid, FortiClient does not connect silently. Instead, it performs the Invalid Certificate Action that is configured in the settings. The Invalid Certificate Action can be set to block, warn, or allow the connection.
Option D is incorrect because default_ZTNARoot CA does not sign the FortiClient certificate for the SSL connectivity to FortiClient EMS. The FortiClient certificate is signed by the ZTNA CA, which is a different certificate authority from default_ZTNARoot CA. default_ZTNARoot CA is the EMS CA Certificate that is used to verify the identity of the EMS server.
[1]: Technical Tip: ZTNA for Corporate hosts with SAML authentication and FortiAuthenticator as IDP
[2]: Zero Trust Network Access - Fortinet
What are the three core principles of ZTA? (Choose three.)
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security model that follows the philosophy of ''never trust, always verify'' and does not assume any implicit trust for any entity within or outside the network perimeter. ZTA is based on a set of core principles that guide its implementation and operation. According to the NIST SP 800-207, the three core principles of ZTA are:
A) Verify and authenticate. This principle emphasizes the importance of strong identification and authentication for all types of principals, including users, devices, and machines. ZTA requires continuous verification of identities and authentication status throughout a session, ideally on each request. It does not rely solely on traditional network location or controls. This includes implementing modern strong multi-factor authentication (MFA) and evaluating additional environmental and contextual signals during authentication processes.
D) Least privilege access. This principle involves granting principals the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. By adopting the principle of least privilege access, organizations can enforce granular access controls, so that principals have access only to the resources necessary to fulfill their roles and responsibilities. This includes implementing just-in-time access provisioning, role-based access controls (RBAC), and regular access reviews to minimize the surface area and the risk of unauthorized access.
E) Assume breach. This principle assumes that the network is always compromised and that attackers can exploit any vulnerability or weakness. Therefore, ZTA adopts a proactive and defensive posture that aims to prevent, detect, and respond to threats in real-time. This includes implementing micro-segmentation, end-to-end encryption, and continuous monitoring and analytics to restrict unnecessary pathways, protect sensitive data, and identify anomalies and potential security events.
1: Understanding Zero Trust principles - AWS Prescriptive Guidance
Exhibit.
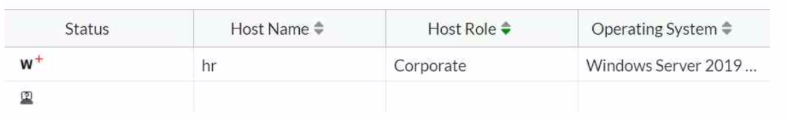
Which two statements are true about the hr endpoint? (Choose two.)
Based on the exhibit, the true statements about the hr endpoint are:
B) The endpoint is marked as a rogue device: The 'w' symbol typically indicates a warning or an at-risk status, which can be associated with an endpoint being marked as rogue due to failing to meet the security compliance requirements or other reasons.
C) The endpoint has failed the compliance scan: The 'w' symbol can also signify that the endpoint has failed a compliance scan, which is a common reason for an endpoint to be marked as at risk.
Which two types of configuration can you associate with a user/host profile on FortiNAC? (Choose two.)