At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE7_NST-7.2 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 7 - Network Security 7.2 Support Engineer exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE7_NST-7.2 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 7 - Network Security 7.2 Support Engineer exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE7_NST-7.2 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the output of diagnose sys session stat. Which statement about the output shown in the exhibit is correct?
Session Table Overview:
The session table in FortiOS tracks all active and pending sessions. It includes details like the type of session (TCP, UDP, etc.), status, and statistics.
Interpreting the Exhibit:
The exhibit from the diagnose sys session stat command shows detailed session statistics.
The specific value indicating '166 TCP sessions waiting to complete the three-way handshake' reflects the number of sessions that have initiated but not yet completed the TCP three-way handshake process (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK).
Fortinet Documentation: Understanding and troubleshooting session tables (Hammertux).
Refer to the exhibits.
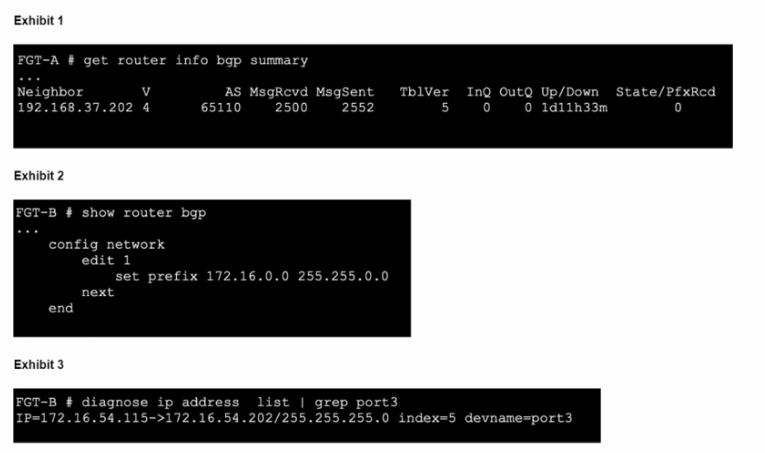
An administrator is attempting to advertise the network configured on port3. However, FGT-A is not receiving the prefix.
Which two actions can the administrator take to fix this problem'' (Choose two.)
Soft Reset of BGP:
Performing a soft reset of BGP is a common method to resolve issues where prefixes are not being received. It forces both BGP peers to resend their complete routing tables to each other.
This can be done using the command: execute router clear bgp soft in and execute router clear bgp soft out.
Network Import Check:
The network-import-check command controls whether the FortiGate should verify that the prefix exists in the routing table before advertising it.
Disabling this check can resolve issues where valid prefixes are not advertised due to stringent verification.
The command to disable this is: config router bgp set network-import-check disable end.
BGP Configuration Verification:
Ensure that the BGP configuration on FGT-B is correctly set to advertise the network 172.16.54.0/24.
Verify that the network statement is correctly configured and matches the intended prefix.
Fortinet Community: Technical Note on Configuring BGP (Welcome to the Fortinet Community!).
Fortinet Documentation: Configuring BGP on FortiGate (Fortinet Document Library).
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a session table entry.
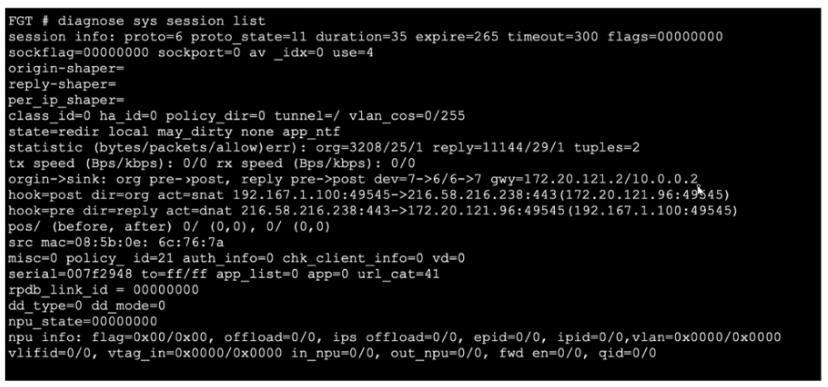
Which statement about FortiGate behavior relating to this session is true?
The session table entry provided shows detailed information about a specific network session passing through the FortiGate device. From the session details, we can see that the session has various attributes such as state, protocol, policy, and inspection details.
The session state (proto_state=11) indicates that the session is being actively processed and inspected.
The npd_state=00000000 suggests that the session is being handled by the CPU rather than offloaded to a Network Processor (NP).
The session is marked for security profile inspection, evident from the detailed byte/packet counts and other session parameters.
From these indicators, it's clear that FortiGate is using its CPU to perform security profile inspection on this session rather than simply forwarding the traffic without inspection or relying solely on IPS inspection.
Fortinet Documentation on Session Table
Fortinet Community Discussion on Session Table
Refer to the exhibit, which shows oneway communication of the downstream FortiGate with the upstream FortiGate within a Security Fabric.
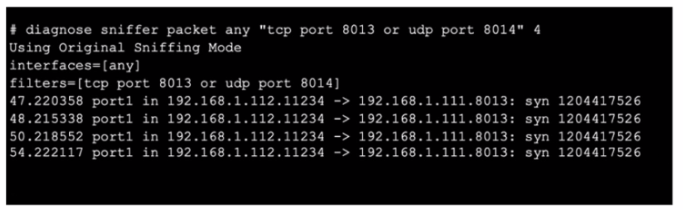
What three actions must you take to ensure successful communication? (Choose three.)
The exhibit shows a sniffer capture where TCP port 8013 is being used for communication. The communication appears one-way, indicating potential issues with the upstream FortiGate receiving the necessary packets or being able to respond.
To ensure successful communication in a Security Fabric setup:
Ensure TCP port 8013 is not blocked along the way: Verify that no firewalls or network devices between the downstream and upstream FortiGates are blocking TCP port 8013. This port is crucial for Security Fabric communication.
Authorize the downstream FortiGate on the root FortiGate: In the Security Fabric, the root FortiGate must recognize and authorize the downstream FortiGate to allow proper communication and management.
Enable Security Fabric/Fortitelemetry on the receiving interface of the upstream FortiGate: The upstream FortiGate must have the Security Fabric or Fortitelemetry enabled on the interface that receives the communication from the downstream FortiGate. This enables proper data exchange and monitoring within the Security Fabric.
Fortinet Documentation on Security Fabric Configuration
Fortinet Community Discussion on Port Requirements
Refer to the exhibit, which shows two entries that were generated in the FSSO collector agent logs.

What three conclusions can you draw from these log entries? (Choose three.)
The exhibit shows log entries from the FSSO (Fortinet Single Sign-On) collector agent logs. These logs provide insights into why there might be issues with the collector agent connecting to workstations or the registry.
Remote registry is not running on the workstation: The failure to connect to the workstation registry can occur if the remote registry service on the workstation is not running. This service needs to be active to allow the FSSO collector agent to query the workstation for user login information.
DNS resolution is unable to resolve the workstation name: The logs indicate a failure in connecting to a workstation by name, which can happen if the DNS server is unable to resolve the workstation's name to an IP address. This is a common issue when the DNS settings are incorrect or the workstation name is not properly registered in the DNS.
A firewall is blocking traffic to port 139 and 445: Communication issues to the workstation or registry are often caused by firewall rules blocking essential ports. Ports 139 (NetBIOS) and 445 (SMB) are critical for these operations. Ensure these ports are open on both the workstation and any intermediate firewalls.
Fortinet Community Documentation on FSSO Troubleshooting
Fortinet Community on FSSO Collector Agent Issues