At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE7_EFW-7.2 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 7 - Enterprise Firewall 7.2 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE7_EFW-7.2 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 7 - Enterprise Firewall 7.2 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE7_EFW-7.2 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Refer to the exhibit.
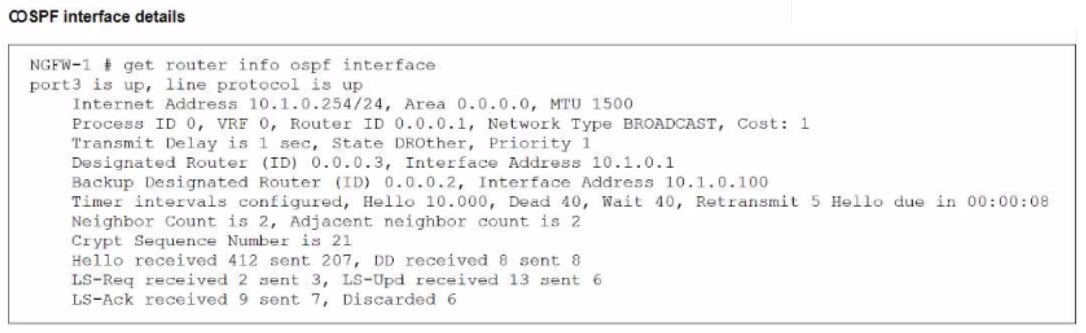
Refer to the exhibit, which shows information about an OSPF interface
What two conclusions can you draw from this command output? (Choose two.)
Which two statements about the BFD parameter in BGP are true? (Choose two.)
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) is a rapid protocol for detecting failures in the forwarding path between two adjacent routers, including interfaces, data links, and forwarding planes. BFD is designed to detect forwarding path failures in a very short amount of time, often less than one second, which is significantly faster than traditional failure detection mechanisms like hold-down timers in routing protocols.
Fortinet supports BFD for BGP, and it can be used over multiple hops, which allows the detection of failures even if the BGP peers are not directly connected. This functionality enhances the ability to maintain stable BGP sessions over a wider network topology and is documented in Fortinet's guides.
Exhibit.
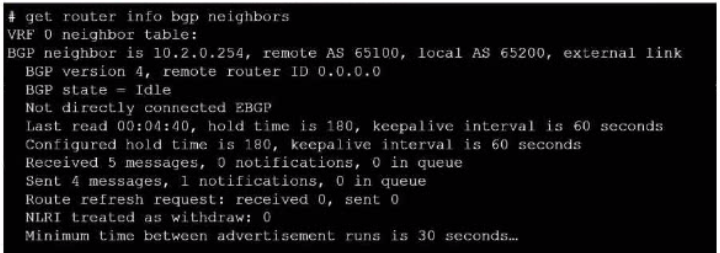
Refer to the exhibit, which provides information on BGP neighbors.
Which can you conclude from this command output?
The BGP state is ''Idle'', indicating that BGP is attempting to establish a TCP connection with the peer. This is the first state in the BGP finite state machine, and it means that no TCP connection has been established yet. If the TCP connection fails, the BGP state will reset to either active or idle, depending on the configuration.Reference: You can find more information about BGP states and troubleshooting in the following Fortinet Enterprise Firewall 7.2 documents:
You contoured an address object on the tool fortiGate in a Security Fabric. This object is not synchronized with a downstream device. Which two reasons could be the cause? (Choose two)
1: Group address objects synchronized from FortiManager5
2: Security Fabric address object unification6
3: Configuration synchronization7
4: Configuration synchronization7
: Security Fabric - Fortinet Documentation