At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE6_WCS-7.0 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 6 - Cloud Security 7.0 for AWS exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE6_WCS-7.0 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 6 - Cloud Security 7.0 for AWS exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE6_WCS-7.0 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
A customer has deployed FortiGate Cloud-Native Firewall (CNF).
Which two statements are correct about policy sets? (Choose two.)
Implicit Deny Rule:
Similar to traditional firewall rule sets, FortiGate Cloud-Native Firewall (CNF) includes an implicit deny rule at the bottom of each policy set. This means any traffic that does not match an existing rule in the policy set is automatically denied (Option A).
Policy Set Creation:
When a new CNF instance is deployed, a new policy set is created specifically for that instance. This ensures that each CNF instance can have a tailored set of security policies based on the specific needs of the deployment (Option C).
Other Options Analysis:
Option B is incorrect because policy sets do not require manual synchronization; they are applied automatically once configured.
Option D is incorrect as a single CNF instance operates with a single policy set at a time.
FortiGate CNF Documentation: FortiGate CNF
Firewall Policy Best Practices: Fortinet Policies
An AWS administrator is designing internet connectivity for an organization's virtual public cloud (VPC). The organization has web servers with private addresses that must be reachable from the internet. The web servers must be highly available.
Which two configurations can you use to ensure the web servers are highly available and reachable from the internet? (Choose two.)
Network Load Balancer:
Deploying a network load balancer ensures that incoming traffic is distributed across multiple web servers, providing high availability and redundancy. This setup helps in managing traffic efficiently and maintaining service uptime even if some servers fail (Option A).
Multiple Availability Zones:
Deploying web servers in multiple availability zones (AZs) enhances fault tolerance and availability. If one AZ goes down, servers in other AZs can continue to handle the traffic, ensuring the web application remains accessible (Option D).
Other Options Analysis:
Option B is incorrect because NAT Gateways are used to provide internet access to instances in private subnets, not to make private addresses reachable from the internet.
Option C is not sufficient on its own for high availability. Adding a route to the default VPC route table forwarding traffic to the internet gateway makes the VPC internet-accessible but does not ensure high availability.
AWS High Availability and Fault Tolerance: AWS High Availability
An administrator has been asked to deploy an active-passive (A-P) FortiGate cluster in the AWS cloud across two availability zones.
In addition to enhanced redundancy, which other major difference is there compared to deploying A-P high availability in the same availability zone?
Enhanced Redundancy:
Deploying an active-passive (A-P) FortiGate cluster across two availability zones (AZs) provides enhanced redundancy by ensuring that if one AZ fails, the other can take over, maintaining high availability and uptime.
IP Addressing and Subnetting:
One of the major differences when deploying across different AZs compared to the same AZ is that IP addressing and subnetting are not shared between the instances. Each AZ operates independently with its own set of subnets and IP addresses, which must be managed separately (Option D).
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is incorrect because the FortiGate devices in an A-P setup do not act as a single logical instance; they operate in a failover setup.
Option B is incorrect because secondary IP address configuration is used in both single AZ and multi-AZ deployments.
Option C is incorrect because the number of subnets required is typically more when deploying across multiple AZs for redundancy.
FortiGate HA Configuration Guide: FortiGate HA
You need to deploy a new Windows server in AWS to offload web traffic from an existing web server in a different availability zone.
According to the AWS shared responsibility model, what three actions must you take to secure the new EC2 instance? (Choose three.)
Update Software:
As part of the AWS shared responsibility model, it is the customer's responsibility to update and maintain the software running on the EC2 instance, including applying security patches and updates (Option A).
Configure Security Groups:
Security groups act as virtual firewalls for instances to control inbound and outbound traffic. Configuring them correctly is essential for securing the EC2 instance and ensuring only legitimate traffic can reach the server (Option C).
Manage Operating System:
Managing the operating system, including user accounts, permissions, and operating system patches, is the responsibility of the customer under the shared responsibility model (Option D).
Other Options Analysis:
Option B is incorrect as changing the existing ELB to a gateway load balancer is not necessary for securing the new EC2 instance.
Option E is incorrect because it is not required to move all web servers into the same availability zone for security purposes.
Refer to the exhibit.
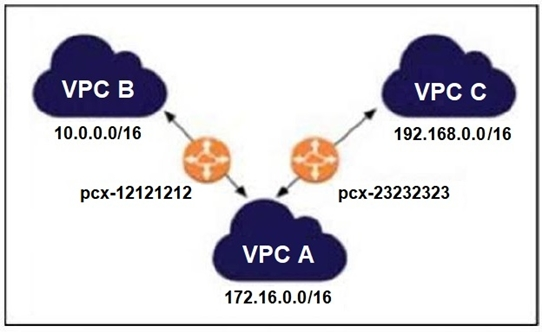
Which statement is correct about the VPC peering connections shown in the exhibit?
Understanding VPC Peering:
VPC peering connections allow instances in one VPC to communicate with instances in another VPC. Peering is a one-to-one relationship between two VPCs.
Transit Routing Limitation:
AWS VPC peering connections do not support transitive peering. This means that a packet originating in VPC B cannot be routed through VPC A to reach VPC C. Each pair of VPCs must have its own peering connection.
Routing Table Configuration:
Even if you add a route in the VPC A routing table for the 192.168.0.0/16 network, it won't allow VPC B to communicate with VPC C because of the non-transitive nature of VPC peering.
Comparison with Other Options:
Option A is incorrect because adding a route in VPC A does not overcome the limitation of non-transitive peering.
Option C is incorrect because associating pcx-23232323 with VPC B is not how VPC peering works.
Option D is incorrect because you can create a separate peering connection between VPC B and VPC C, which is the required approach for communication between these VPCs.