At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
An administrator is checking an enterprise network and sees a suspicious packet with the MAC address e0:23:ff:fc:00:86.
What two conclusions can the administrator draw? (Choose two.)
The MAC address e0:23:ff:fc:00:86 follows the format used in FortiGate High Availability (HA) clusters. When FortiGate devices are in an HA configuration, they use virtual MAC addresses for failover and redundancy purposes.
The suspicious packet is related to a cluster that has VDOMs enabled: FortiGate devices with Virtual Domains (VDOMs) enabled use specific MAC address ranges to differentiate HA-related traffic. This MAC address is likely part of that mechanism.
The suspicious packet is related to a cluster with a group-id value lower than 255: FortiGate HA clusters assign virtual MAC addresses based on the group ID. The last octet (00:86) corresponds to a group ID that is below 255, confirming this option.
An administrator must standardize the deployment of FortiGate devices across branches with consistent interface roles and policy packages using FortiManager.
What is the recommended best practice for interface assignment in this scenario?
When standardizing the deployment of FortiGate devices across branches using FortiManager, the best practice is to use metadata variables. This allows for dynamic interface configuration while maintaining a single, consistent policy package for all branches.
Metadata variables in FortiManager enable interface roles and configurations to be dynamically assigned based on the specific FortiGate device.
This ensures scalability and consistent security policy enforcement across all branches without manually adjusting interface settings for each device.
When a new branch FortiGate is deployed, metadata variables automatically map to the correct physical interfaces, reducing manual configuration errors.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the ADVPN network topology and partial BGP configuration.
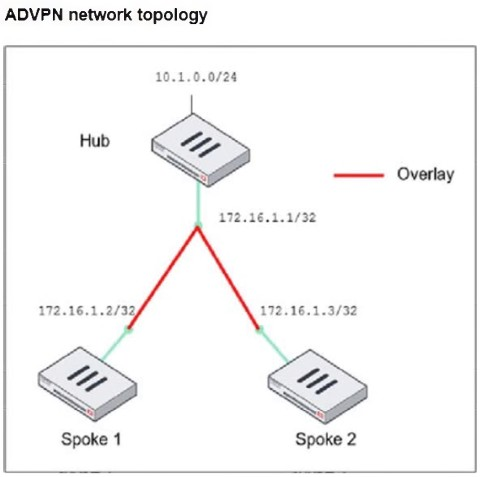

Which two parameters must an administrator configure in the config neighbor range for spokes shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
In the given ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) topology, BGP is being used to dynamically establish routes between spokes. The neighbor-range configuration is crucial for simplifying BGP peer setup by automatically assigning neighbors based on their IP range.
set neighbor-group advpn
The neighbor-group parameter is used to apply pre-defined settings (such as AS number) to dynamically discovered BGP neighbors.
The advpn neighbor-group is already defined in the configuration, and assigning it to the neighbor-range ensures consistent BGP settings for all spoke neighbors.
set prefix 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
This command allows dynamic BGP peer discovery by defining a range of potential neighbor IPs (172.16.1.1 - 172.16.1.255).
Since each spoke has a unique /32 IP within this subnet, this ensures that any spoke within the 172.16.1.0/24 range can automatically establish a BGP session with the hub.
An administrator must enable direct communication between multiple spokes in a company's network. Each spoke has more than one internet connection.
The requirement is for the spokes to connect directly without passing through the hub, and for the links to automatically switch to the best available connection.
How can this automatic detection and optimal link utilization between spokes be achieved?
ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) 2.0 is the optimal solution for enabling direct spoke-to-spoke communication without passing through the hub, while also allowing automatic link selection based on quality metrics.
Dynamic Direct Tunnels:
ADVPN 2.0 allows spokes to establish direct IPsec tunnels dynamically based on traffic patterns, reducing latency and improving performance.
Unlike static VPNs, spokes do not need to pre-configure tunnels for each other.
Automatic Link Optimization:
ADVPN 2.0 monitors the quality of multiple internet connections on each spoke.
It automatically switches to the best available connection when the primary link degrades or fails.
This is achieved by dynamically adjusting BGP-based routing or leveraging SD-WAN integration.
An administrator configured the FortiGate devices in an enterprise network to join the Fortinet Security Fabric. The administrator has a list of IP addresses that must be blocked by the data center firewall. This list is updated daily.
How can the administrator automate a firewall policy with the daily updated list?
The best way to automate a firewall policy using a daily updated list of IP addresses is by using an external connector from Threat Feeds. This allows FortiGate to dynamically retrieve real-time threat intelligence from external sources and apply it directly to security policies.
By configuring Threat Feeds, the administrator can:
Automatically update firewall policies with the latest malicious IPs daily.
Block traffic from those IPs in real-time without manual intervention.
Integrate with FortiGuard, third-party threat intelligence sources, or custom feeds (CSV, STIX/TAXII, etc.).