At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the CompTIA DA0-001 exam questions by CompTIA. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the CompTIA Data+ Certification Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by CompTIA in their CompTIA DA0-001 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their CompTIA Data+ Certification Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the CompTIA DA0-001 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
A data architect is designing a data solution for a retail clothing store chain. Each store has a database that tracks sales transactions. The data architect needs to create a summary table that will be used for a senior executive dashboard. The summary table should not contain duplicate store information. Which of the following should the data architect create?
A unique constraint ensures that no duplicate values exist in a specified column of a table. This is essential for creating summary tables where each store should only appear once in the dataset.
Which of the following is the best technique for transferring data from one database to another with some data manipulation?
An analyst must obtain the average daily sales for the following week:
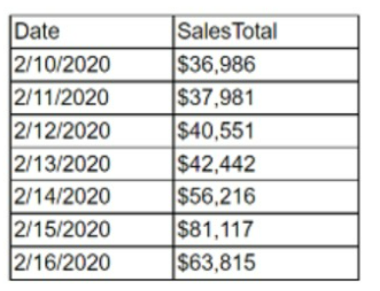
Which of the following must the analyst perform to obtain this value?
Data aggregation is the process of compiling data from multiple sources and summarizing it into a single dataset. Data aggregation can be used to calculate statistics, such as averages, sums, counts, or percentages. In this case, the analyst must obtain the average daily sales for the following week, which is a statistic that can be calculated by aggregating the sales data from each day and dividing by the number of days. Data aggregation can be done using various tools and methods, such as spreadsheets, databases, or programming languages.
Which one of the following values will appear first if they are sorted in descending order?
The value that will appear first if they are sorted in descending order is Xavier. Descending order means arranging values from the largest to the smallest, or from the last to the first in alphabetical order. In this case, Xavier is the last name in alphabetical order, so it will appear first when sorted in descending order. The other names will appear in the following order: Molly, Adam, Aaron. Reference:Sorting Data - W3Schools
Which of the following would be considered non-personally identifiable information?
Non-personally identifiable information (non-PII) is any data that cannot be used to identify, contact, or locate a specific individual, either alone or combined with other sources. Non-PII can include aggregated statistics, anonymous data, device identifiers, IP addresses, cookies, and other types of information that do not reveal the identity or location of a person. Cell phone device name is an example of non-PII, as it does not reveal any personal information about the owner or user of the device. Therefore, the correct answer is A. Reference: What is Non-Personally Identifiable Information (Non-PII)? | Definition and Examples, What is Personally Identifiable Information (PII)? | Definition and Examples