At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the AGA CGFM exam questions by AGA. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the AGA Certified Government Financial Manager exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by AGA in their AGA CGFM exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their AGA Certified Government Financial Manager exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the AGA CGFM exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
What is the most fupdamental cash control?
Cash Control Fundamentals:
The primary goal of cash controls is to safeguard assets and prevent fraud, errors, or misappropriation.
Frequent bank reconciliations ensure that recorded cash balances match actual bank balances, detecting discrepancies quickly.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A . Segregation of duties: While critical for cash management, it is not the most fundamental cash control.
B . Use of automated systems: Helpful for efficiency but not a fundamental control.
C . Analysis of cash reports: Important, but reconciling bank accounts is more critical for detecting errors or fraud.
D . Frequent reconciliation of bank accounts: Correct. This is the most fundamental and widely recognized control for safeguarding cash.
Association of Government Accountants (AGA), Cash Management Best Practices.
Government Finance Officers Association (GFOA), Bank Reconciliation Best Practices.
Based on the data below, what can be concluded about outsourcing print job?
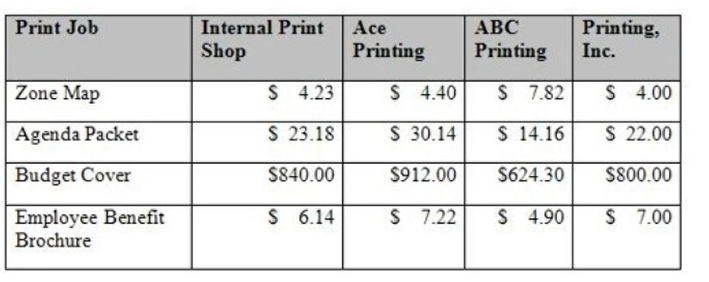
Understanding the Scenario: The table compares the costs of four printing jobs performed by an 'Internal Print Shop' versus three external vendors (Ace Printing, ABC Printing, and Printing, Inc.). Each vendor's pricing varies by print job type. The task is to evaluate whether outsourcing (hiring external vendors) is a reasonable alternative to keeping the work in-house.
Key Considerations in Outsourcing: According to governmental accounting principles and budgeting practices outlined by the Association of Government Accountants (AGA), the decision to outsource should consider:
Cost-effectiveness: Does outsourcing reduce costs without compromising quality or service delivery?
Operational efficiency: Can outsourcing free up internal resources for other priorities?
Comparative pricing: How do external vendor rates compare to internal costs for identical services?
Analysis of the Print Jobs: Let's break down the cost comparison for each print job:
Zone Map: Internal cost = $4.23. Cheapest vendor = Printing, Inc., at $4.00. Outsourcing is cheaper for this job.
Agenda Packet: Internal cost = $23.18. Cheapest vendor = Printing, Inc., at $22.00. Outsourcing is cheaper for this job.
Budget Cover: Internal cost = $840.00. Cheapest vendor = ABC Printing, at $624.30. Outsourcing is significantly cheaper for this job.
Employee Benefit Brochure: Internal cost = $6.14. Cheapest vendor = ABC Printing, at $4.90. Outsourcing is cheaper for this job.
Conclusion Based on Analysis:
Across all four print jobs, the lowest-cost external vendor always beats the Internal Print Shop's costs.
From a budgetary perspective, outsourcing is feasible as it offers cost savings across all jobs.
Why Not A, C, or D?:
Option A (Keep printing in-house): Incorrect, as in-house costs are consistently higher than the cheapest external vendor.
Option C (Outsourcing is necessary): Incorrect, as feasibility doesn't mean necessity; internal printing is still an option if other factors (like quality or control) outweigh costs.
Option D (Award contract to ABC Printing): Incorrect, since the best vendor depends on the job (e.g., Printing, Inc. is cheaper for Zone Map and Agenda Packet).
Association of Government Accountants (AGA), Government Financial Manager Certification Study Guide: Budgeting, Cost Accounting, and Auditing Principles.
Government Finance Officers Association (GFOA), Best Practices in Outsourcing and Procurement.
Federal Accounting Standards Advisory Board (FASAB), Cost Accounting Standards for Governmental Operations.
According to the GAO, internal control is a process used by management to
Definition of Internal Control (According to GAO):
Internal control is a process implemented by management to provide reasonable assurance that the organization will achieve its objectives in:
Operations (effectiveness and efficiency).
Reporting (reliable and accurate financial and non-financial reporting).
Compliance (adherence to laws and regulations).
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A . Help an entity achieve its objectives: Correct. This is the primary purpose of internal controls.
B . Design an ERM system: Incorrect. Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is broader than internal control and includes risk strategy and appetite.
C . Set the tone at the top: Incorrect. While the tone at the top is part of the control environment, it is not the full scope of internal control.
D . Develop a strategic plan: Incorrect. Internal control supports strategic plans but is not directly involved in developing them.
GAO, Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government (Green Book).
COSO, Internal Control - Integrated Framework.
The four general government auditing standards are
What Are the Four General Government Auditing Standards?
These standards, as defined in the GAO Yellow Book (Government Auditing Standards):
Qualifications: Auditors must have the necessary professional skills and competence to perform their work.
Independence: Auditors must remain free from personal, external, and organizational impairments to maintain objectivity.
Due Professional Care: Auditors must exercise care and diligence, adhering to professional standards and ethical requirements.
Quality Control: Auditors must establish and maintain a system of quality control to ensure audit work meets professional standards.
Why Is Option D Correct?
These four elements are explicitly outlined in the GAO Yellow Book as the core principles of government auditing standards.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A . Compliance, timeliness, qualifications, and due professional care: Timeliness and compliance are not part of the four general standards; they are components of audit objectives.
B . Supervision, planning, management controls, and evidence: These are aspects of audit performance, not general standards.
C . Planning, internal controls, independence, and irregularities: Planning and internal controls are part of the audit process, not general standards.
Reference and Documents:
GAO Yellow Book (Generally Accepted Government Auditing Standards - GAGAS): Lists qualifications, independence, due professional care, and quality control as the four general standards.
AICPA Audit Standards: Aligns with GAGAS in emphasizing these four principles.
A city parks department is selecting a contractor to renovate a community playground. Which of the following contractors should be selected?
Understanding the Procurement Process for Contractors:
When selecting contractors for government projects, the goal is to ensure the selection of a responsible and responsive bidder who meets all requirements outlined in the Request for Proposal (RFP) or bidding documents.
Key considerations include the contractor's ability to meet deadlines, quality of work, and compliance with laws and regulations.
Analyzing the Answer Options:
A . The contractor with the lowest bid who has a history of delayed projects:
While cost savings are important, a contractor with a history of delays poses a significant risk to project timelines and community satisfaction. This bidder is not considered 'responsible' based on their track record.
B . The contractor with the second-lowest bid, who has no prior violations and meets all bid specifications:
Although this is not the lowest bid, it is the best choice because the contractor meets all requirements and has a clean history. Selecting a reliable bidder ensures the project is completed on time and within acceptable quality standards. This is the most responsible and justified decision.
C . The contractor with the highest bid, who includes luxury, non-requested upgrades to the design:
Selecting a contractor who proposes unnecessary and expensive upgrades is not cost-effective. Government procurement prioritizes fulfilling project specifications within the approved budget, making this choice impractical.
D . The contractor whose bid was submitted past the deadline but offers a discount for early payment:
Late bids violate procurement rules, which emphasize fairness and transparency. Accepting this bid could lead to legal challenges or allegations of favoritism. Discounts do not justify breaching procurement guidelines.
Why Option B is Correct:
The second-lowest bid is the most responsible choice because the contractor:
Meets all bid requirements.
Has a strong history of compliance with regulations.
Avoids risks associated with unreliable or excessively expensive options.
This selection aligns with government procurement standards that prioritize balancing cost, quality, and reliability.
Reference and Documentation from the Government Financial Manager (GFM) by AGA:
Procurement Best Practices: The AGA emphasizes the importance of selecting bidders who demonstrate responsibility, reliability, and compliance with the bidding process.
Ethical Procurement Standards: The Yellow Book (Government Auditing Standards) highlights the importance of fairness, transparency, and accountability in contractor selection.
Source: AGA Certified Government Financial Manager (CGFM) study guides, Section IV: Internal Controls, Procurement, and Ethics.